What is Requirements Management?
The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Chapter 1: What is Requirements Management?
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
What is Requirements Management?
Requirements management is the structured process of gathering, analyzing, verifying, and validating the needs and requirements for a given product or system throughout its lifecycle.
Effective requirements management ensures that stakeholders’ expectations are clearly understood and that the final deliverables effectively meet these expectations. By maintaining alignment between stakeholder needs and the product being developed, it minimizes risks, enhances product quality, and drives project success.
Whether you’re new to requirements management, seeking to enhance your current process, or aiming to benchmark against industry leaders, this guide has you covered.
In this article, we’ll explore what requirements management is, why it’s essential, the key steps in the process, and how to effectively manage requirements for complex, highly regulated products.
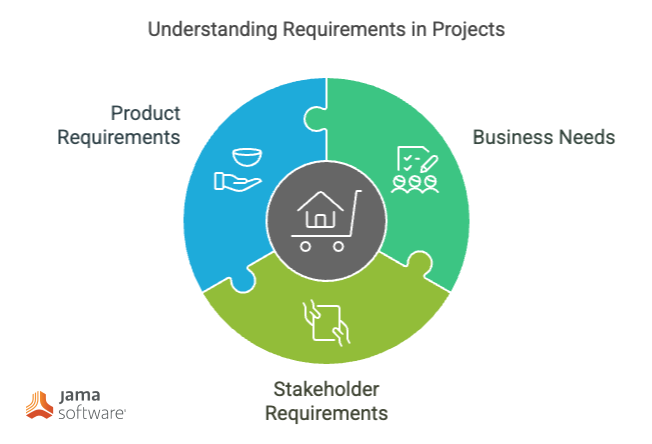
What is a need?
A need is an agreed-to expectation for a product or system to perform some function or possess some quality within specified constraints with acceptable risk. Needs communicate what the stakeholders need and expect from a product or system in order for a given problem or opportunity to be addressed.
What is a requirement?
A requirement is the result of a formal transformation of one or more needs or parent requirements into an agreed-to obligation for a product or system to perform some function or possess some quality within specified constraints with acceptable risk.
There are different types of needs and requirements that range from a business focus to a user focus to a technical focus.
Business needs and requirements, sometimes referred to as stakeholder needs and requirements, are those derived from the business processes or elicited from the stakeholders including customers, users, and other stakeholders involved in the project. The stakeholder needs represent what the stakeholders need the product to do to address the problem or opportunity the product is to address; stakeholder requirements are stakeholder-defined product requirements that communicate what the stakeholders require of the product to meet their needs. Stakeholder needs are expressed in natural language without the use of “shall”, while stakeholder requirements are communicated with “shall” to make sure they are treated as binding requirements the product will be verified to meet.
Given there are multiple stakeholders, there will be multiple sets of stakeholder needs and requirements. It is up to the project team to elicit these needs and requirements, and resolve conflicts, inconsistencies, and other issues. The results will be an integrated set of needs from which the product requirements will be transformed. The resulting product requirements represents what the product must do in order for the needs to be met. Product requirements are sometimes referred to as system requirements, software requirements, or technical requirements.
What is requirements management?
Requirements management is the process of gathering, analyzing, verifying, and validating the needs and requirements for the given product or system being developed. Successful requirements management ensures that completed deliverables meet the expectations of the stakeholders. Requirements can be managed using documents, however, complex systems or products in highly regulated industries mitigate risk by using trusted requirements management tools.
Why is requirements management important?
Requirements management is important because it empowers everyone to clearly understand stakeholder expectations and confidently deliver a product that has been verified to meet the requirements and validated to meet the needs.
Requirements management is a sophisticated process that includes many moving parts and diverse groups of people. Typically, the product management department, specifically the product manager, is responsible for the requirements management process. They work with the stakeholders, including business teams, customers, users, developers, testers, regulators, and quality assurance.
Additionally, a product may have only 100 requirements, or it may have several thousand. This number will depend on the product’s complexity and level of regulation. With all these elements at play, success hinges on the ability to get everyone on the same page, working toward the same goal.
Therefore, the business value of managing requirements is huge, as successful requirements management is key to project success. Benefits of requirements management include:
- Enhance understanding of stakeholder needs, requirements, and expectations and the problem or opportunity the product means to address
- Gain clarity on scope, budget, and schedule
- Minimize costly, time-consuming rework
- Increase product quality
- Mitigate risk
- Improve likelihood of delivering the right product, within budget and schedule with the required quality.
The importance of requirements management is intensified, however, when building complex or highly regulated products. This is because more time and budget are invested in development. The cost of getting it wrong — be it money, time, or reputation — is too great to risk. Hence, developers in regulated industries, or those who develop products with a lengthy list of needs and requirements, tend to rely on requirements management tools, like Jama Connect® to keep their projects in order.
Requirements management vs. project management
While it may seem that requirements management and project management are synonymous, there is a difference. Simply, project management is getting the product built within budget and schedule with the available resources. Requirements management is making sure the product is the right product and that it is built right.
The goal of the product development process is to create a successful product that meets stakeholder, customer, and market needs. The requirements management piece of product development includes managing the needs and requirements so that the product meets stakeholder expectations. Therefore, needs and requirements along with budget and schedule set the scope for the project.
However, the domain of project management encompasses tasks like providing budget, personnel, and resources needed to develop the product.
Ready to Find Out More?
Our team of experts is here to answer any questions and learn how we can help enable your continued success. Get started with a free 30-day trial, or book a demo!
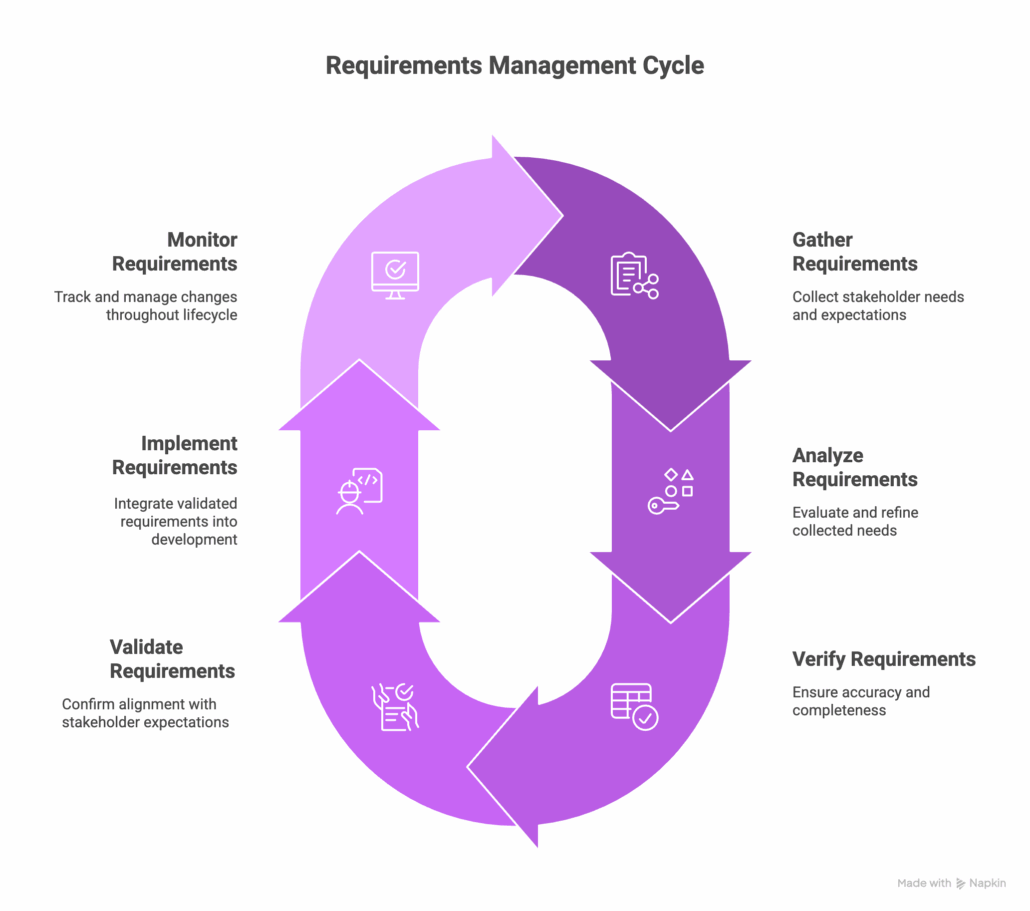
Understand the Four Stages of Requirements Management
A solid requirements management process ensures your team delivers high-quality products that meet stakeholder needs—on time and within budget. The four key stages—planning, development, verification, and validation—provide a structured approach to managing evolving requirements. Modern tools like Jama Connect simplify collaboration, automate compliance, and improve traceability, helping you overcome common challenges.
Learn more and take control of your process: Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
Requirements development stage
The development stage is conducted using the organization’s requirements analysis process.
The needs and requirements development stage includes eliciting needs and requirements from the identified stakeholders, properly defining and refining them, and analyzing them to ensure clarity and resolve issues and conflicts. Without successful needs and requirements development, there would very likely be gaps between what stakeholders were expecting and what is ultimately delivered, which could ultimately result in disaster.
Eliciting needs and requirements
Needs and requirements elicitation – also called needs and requirements gathering – is the act of working with users, customers, and internal business stakeholders to identify stakeholder needs and requirements and get an understanding of the requirements for a product or system.
Needs and requirements definition
Needs and requirements definition is the time when the gathered needs and requirements are re-written in a clear and traceable way that enables effective communication throughout the product development lifecycle.
There are many do’s and don’ts for writing needs and requirements, but the following are basic characteristics of quality needs and requirements:
- Necessary
- Unambiguous
- Feasible
- Verifiable
- Correct
- Traceable
- Appropriate
Traceability of needs and requirements is very important. At the end of the day, traceability is the only way to know if a need or requirement has been fulfilled by the design and the built product. Bi-directional traceability—the ability to perform both forward and backward traceability, usually made possible via requirements management tools like Jama Connect—allows teams to understand why a specific need or requirement exists and easily analyze the impact of changes.
Furthermore, products in regulated industries must demonstrate traceability to prove compliance with standards and regulations. Therefore, when writing requirements, it’s paramount that each requirement maps to all corresponding artifacts.
Many teams use a requirements traceability matrix (RTM) to track requirements and manage the scope of a requirements change. The RTM is static and maintained manually. The problem is that change is ubiquitous in the product development process. When change happens, teams must manually search the RTM document for all related upstream and downstream needs and requirements, dependent requirements, and verification and validation tests that may be affected by the change.
Scouring through an excel spreadsheet for each change may not be that daunting if there are only one hundred or so needs and requirements. However, if the product has hundreds or thousands of needs and requirements—think complex, regulated products—managing the scope of change becomes a cumbersome and time-draining exercise fraught with risk.
Requirements management tools are designed to streamline the process—even for highly complex, regulated products. Jama Connect, specifically, uses the benefits of Live Traceabilty™ to:
- Easily determine the impact of change
- Automate compliance
- Enable end-to-end process improvement
- Increase productivity
- Reduce product risk
- Increase quality
Requirements analysis
Sometimes, there is a gap between what stakeholders say they want and what they actually want. The purpose of requirements analysis is to ensure all business, software, and product requirements accurately represent stakeholder needs and requirements. The goal of requirements analysis is to get a clear understanding of stakeholder needs so the deliverable matches stakeholder expectations.
System Verification Stage
System verification means determining if the finished product meets the baselined product requirements. This is different than system validation (discussed below), which evaluates whether the product satisfies the stakeholder needs. Both are important, but system verification always comes first.
Planning for this stage starts when the product requirements are being defined. Planning includes determining which system verification events are needed to confirm that product requirements are fulfilled.
To ensure successful system verification, the following attributes should be defined for each product requirement before the requirements are baseline.
- Success criteria (what must be proven to show the requirement was met)
- Method (test, demonstration, inspection, or analysis)
- Strategy (approach to be used, operating environment, test environment, system configuration, etc.)
Defining these attributes sets the expectations for the test and quality assurance work that needs to be done, and reduces the risk of rework down the line.
System Validation Stage
System validation means determining whether the product satisfies its established stakeholder needs. Successful system validation is what leads to acceptance of the product for its intended use by its intended users in the actual operational environment. For highly regulated products, approval for use is dependent upon successful system validation. Final product acceptance by a customer also depends on successful system validation.
Planning for system validation starts when the integrated set of needs are being defined. Planning includes, determining which system validation events are needed to confirm that needs are fulfilled. One approach is to define a set of attributes that address system validation for each need.
To ensure successful system validation, the following attributes should be defined for each need before the needs are baselined.
- Success criteria (what must be proven to show the need was met)
- Method (test, demonstration, inspection, or analysis)
- Strategy (approach to be used, operating environment, test environment, system configuration, etc.)
Defining these attributes sets the expectations for the test and quality assurance work that needs to be done, and reduces the risk of rework down the line.
Challenges with requirements management
Requirements management has its share of challenges. One such challenge is change management. Because change is so prevalent in the requirements management process, teams need to address how they will manage change at the beginning of the project.
When building products that have thousands of requirements and countless changes, teams can spend hours circulating, editing, and tracking changes in an attempt to maintain traceability and simply keep development on track.
This is especially challenging when maintaining the needs and requirements in document form. Version control issues are one challenge that results from change. Versioning problems can arise on the artifact itself. For example, someone might be giving feedback on SRS version one but there is already an SRS version two with different, additional edits. What’s more, version control can be even more granular within the document as well. For example, requirement one might be on version three, which is linked to test B on version two.
Add to that consolidating feedback from multiple stakeholders via email or meetings, analyzing the impact of change across various versions of requirements artifacts, and communicating the correct changes and statuses to the right people. It’s a nightmare just thinking about how to keep it all straight.
The following are the top five challenges of requirements management:
- Last-minute feedback
- Decision rehashing
- Change tax
- Attention deficit
- Mismatched expectations
It’s easy to recognize that problems are compounded when managing requirements using documents – or legacy systems based on documents – instead of a purpose-built requirements management tool. Most of these challenges, and more, can be overcome by switching from a document-centric to a data-centric approach to requirements management to one that is data-centric.
How to successfully manage requirements in complex products and highly regulated industries
The challenges above are real and mastering them can have significant impact on development timelines and budget. Developers in regulated industries — like automotive, aerospace, medical device, government, and industrial manufacturing — are further challenged by the need to prove compliance with regulations and standards.
Standards and regulations can be sources of hundreds of requirements with which a product must comply. Often, not all of the requirements in a regulation or standard apply to your specific product. Standards and regulations contain requirements not only for products, but also requirements concerning system verification and system validation (acceptance, certification, and qualification), and requirements. On the organization developing the product, as well. In addition, requirements within standards and regulations are often poorly written and ambiguous.
When identifying drivers and constraints at the beginning of the project, the project team needs to identify all applicable standards and regulations which requirements within those standards and regulations actually apply to their specific product. Then, they must write well-formed product requirements to address the intent of those regulatory requirements, such that the product will result compliant with the applicable standards and regulations.
Regulations are not requirements. Requirements must be written to adequately satisfy the regulatory standards. A keen understanding of applicable standards and regulations is paramount in writing requirements that will lead to a product’s compliance. Once written, a regulatory requirement should be attributed as such in all requirements artifacts. This can be done be assigning a “compliance” attribute. This provides all team members visibility throughout development, which assists with decision making and change analysis.
In addition to expert knowledge of the standards and regulations, the following are needed to maintain product compliance when building a product:
- Collaboration between teams
- Single source of truth for defining, verifying, and validating compliance requirements
- Standard frameworks aligned to standards and regulations
- Traceability across all development activities and resulting artifacts.
- Simplified audit preparation and data exports
Reporting is key when faced with a compliance audit. Teams must know what data is required for the audit and how to easily access it when needed. Often, audit trails are an afterthought in which teams are scrambling to pull together data from several sources. This is a dangerous practice, though, because it can put delivery timelines and launch deadlines at risk. It can even put the launch at risk of failing altogether. Teams that must demonstrate compliance, must eliminate this risk with a detailed, digital audit trail that can be easily exported whenever needed. Establishing and managing traceability is critical to maintaining the audit trail.
Many leaders in regulated industries rely on requirements management tools to reduce the risk of failure to comply with standards and regulations during the product development process. Jama Connect, for example, can track standards and regulations and compliance when building products. These industry leaders leverage Jama Connect to keep them at the forefront of innovation:
RELATED ARTICLE: Evaluating Requirements Management Tools
Benefits of requirements management tools
- The advantages of RM tools are many. A modern solution can eliminate the risks and inefficiencies of documents and legacy systems.A valuable RM system, like Jama Connect, can bridge engineering silos throughout the development process, including test and risk activities. An effective requirements management tool helps improve the product development process by:
- Ensuring quality and compliance
- Managing risk
- Increasing efficiency and optimizing processes
- Making it easy to understand and respond to change
- Improving traceability
- Streamlining and accelerating reviews
- Enabling real-time collaboration and iteration
- Saving time
- Improving quality
There are many requirements management tools available, but only a few that can help reap all the benefits listed above. When thinking about the most important features in a requirements management system, first think about what’s being built. The industry and complexity level will help inform the features that will be best for your team. This guide to buying a requirements management tool may also help.
From our experience, and what we hear from customers, the most important features of a requirements management system are:
- Live bidirectional traceability
- Real-time collaboration communication
- Efficient and scalable review process
- Simplified test and quality assurance management
- Always-on risk analysis
- Reusable requirements and baseline catalogs
- Standardized validation and functional safety kits
- Comprehensive visibility and compliance reporting
- Fast implementation
- Flexible configuration
- Easy-to-use interface/administration
- Automated integrations
- Quality assessment of requirements and traceability
The good news is that you don’t have to pick and choose. Jama Connect helps navigate complexity and provides end-to-end compliance, risk mitigation, and process improvement with all the features listed above—and more.
See how Jama Connect can streamline complex requirements management.
In This Webinar, Learn More About the High Cost of Poor Requirements Management
Requirements Management is the process of gathering, analyzing, verifying, and validating the needs and requirements for the given product or system being developed. Successful requirements management ensures that completed deliverables meet the expectations of the stakeholders.
Book a Demo
See Jama Connect in Action!
Our Jama Connect experts are ready to guide you through a personalized demo, answer your questions, and show you how Jama Connect can help you identify risks, improve cross-team collaboration, and drive faster time to market.