In this blog, we recap our webinar, “Accelerate Your ECSS Standards Compliance with Jama Connect®“. Click HERE to watch the entire thing.
Streamline your systems engineering efforts and ensure your products meet all the necessary industry standards.
Jama Connect® enables digital transformation with a more efficient and user-friendly approach to managing space systems development. It can optimize your systems engineering efforts and ensure your products meet all the necessary industry standards.
Learn how to incorporate regulations governing European space systems development into your Jama Connect solution. In this webinar, we discuss how customers can leverage a library of the European Cooperation for Space Standardization (ECSS) standards right inside their Jama Connect instance.
Cary Bryczek, Director of Aerospace & Defense (A&D) Solutions at Jama Software® along with fellow A&D experts Alisa Eikanas and Martijn Janssen, provide a high-level overview of the ECSS standards, along with best practices for leveraging them within Jama Connect, including:
- ECSS Process workflows and how they align with processes managed within Jama Connect
- Establishing an ECSS Library in Jama Connect to provide a Single Source of Truth
- Explanation on how to tailor the ECSS requirements and leverage Jama Connect’s Reuse capability
Below is an abbreviated transcript of our webinar.
Accelerate Your ECSS Standards Compliance with Jama Connect®
Cary Bryczek: So welcome to today’s webinar. I am Cary Bryczek, the Director of Aerospace and Defense Solutions. I lead up a global team of industry and Jama Connect experts. For today’s webinar, two esteemed members of the team will be speaking. First to speak is Martijn Janssen. Martijn is a senior consultant at Jama Software. He has been working with PLM and requirements management solutions for over 15 years and is very proficient in not only Jama Connect but the Siemens industry software solutions as well as PTC Windchill. He currently works on implementing space-related systems such as satellites, launchers, and space-related components in the European Union for our Jama Connect partners. Martijn is a specialist in both systems engineering and information technologies.
We are also joined by Alisa Eikanas. Alisa is a senior consultant at Jama Software. She has over 15 years of experience supporting multi-discipline engineering teams and brings more than 10 years of experience as a business analyst to Jama’s customers. She works with our largest US government and commercial space customers in the US and she’s an expert at helping customers migrate data from legacy requirements tools such as Doors to Jama Connect. And with that, I’ll pass it over to you Martijn.
RELATED: Jama Connect® for Space Systems Datasheet
Martijn Janssen: Well, thank you for the introduction there, Cary. So welcome everybody to our webinar on ECSS. I’m very excited today to introduce you to the way we manage ECSS standards within Jama Connect. Over the past couple of years, we’ve been working with a lot of customers on managing ECSS standards within our solutions, and today we’re going to show you some examples of how we manage to do that.
So without further ado, I’m going to go over some of the ECSS standards, which include, the use cases our customers face, and then afterward Alisa will dive into the system and show you some of those use cases in action in Jama Connect. Let’s dive into the presentation.
When we talk about ECSS, and I presume many of you here already are aware, but for those of you that are not aware of ECSS, ECSS is a European Cooperation and it’s a collaboration between the ESA, the European Space Agency, and many different other space agencies across the world to make sure that we have a single set of standards that we can use across companies working in the European space activities. Many of our customers around the world are looking to those standards, making sure they’re compliant with them, and working with those standards in different projects and at different levels.
So ECSS is a standard. You can find a lot of information on the website for ESA about the standards. They’re all there to be found if you’re not aware of them already. The way that ECSS is organized and set up is something you will see in the standards on the website itself, but we also have the organization within our Jama Connect application. So once Alisa’s going to show the demo, you will recognize a lot of those structures in Jama Connect.
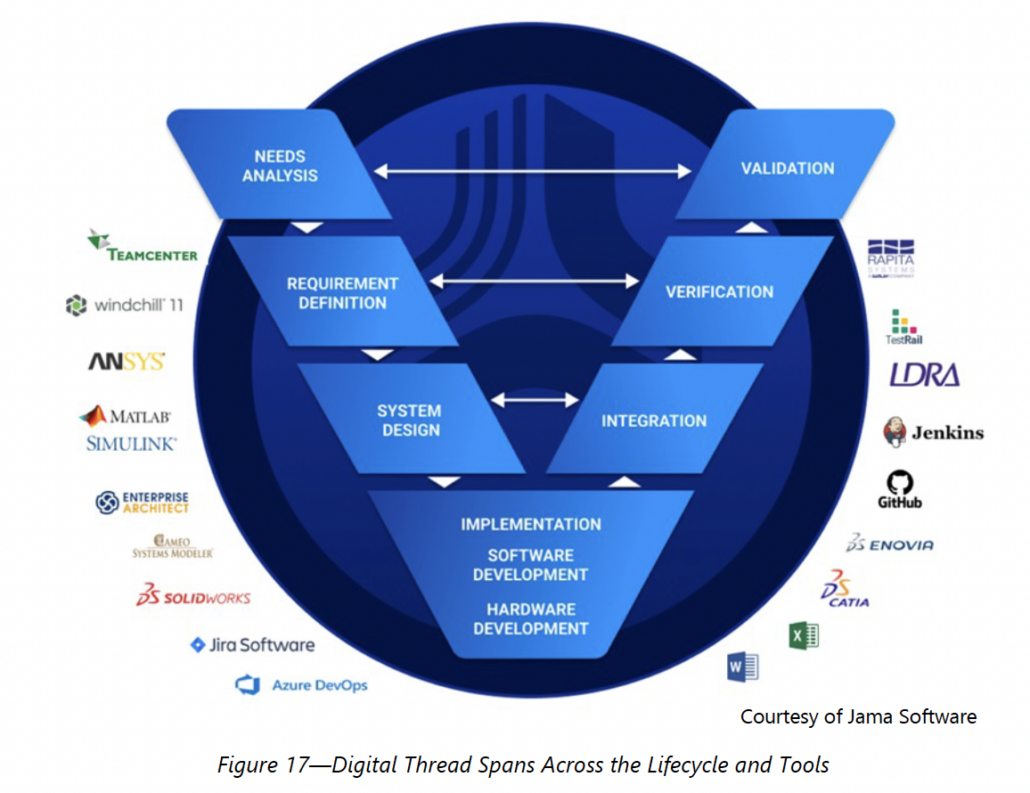
RELATED: CIMdata: Digital Thread in Aerospace and Defense
Janssen: So when we talk about the standards, the standards are divided into branches and disciplines. So you will find, for example, the different branches on the top level there. So for example, the space project management branch or the engineering branch. Below those branches, you will find a lot of disciplines detailed per section. They are numbered in a specific way. Again, when we look into the demo, you will see a lot of those specific annotations come back and we maintained that same structure within Jama. So many of our customers use a subset or a number of these standards in their Jama Connect application to make sure they are compliant and they are working towards the standards that ESA has set for these specific projects. So the main structure in here is recognizable towards what is on the websites and in the organization of ECSS.
Outside of the actual organization of the disciplines and the branches, the disciplines themselves are even further, let’s say detailed in documents. All these documents fall into one of those disciplines. So for example, when we look at the discipline of system engineering, you can see a large number of documents below that, talk about different topics. So for example, on testing, on verification, on referencing coordinate systems, all kinds of documents describing the standard, what you need to do to be compliant towards those standards.
Now these documents are pulled into Jama Connect. And as you will see later on, we have all these documents available for you to start tracking and tracing compliance. So the structure from a branch to a discipline to all the documents is something that you will recognize in the demo later on by Alisa and where you can find and filter and search for certain topics that are numbered and maintained by the ESA.
To watch the entire webinar, visit:
Accelerate Your ECSS Standards Compliance with Jama Connect®