In this blog, we recap The New ARP4754B and Techniques in Jama Connect for Airborne Systems Whitepaper.
The New ARP4754B and Techniques in Jama Connect® for Airborne Systems
ARP4754B, released on December 20, 2023, is a standard from SAE International that provides recommendations for the development of civil aircraft and systems, focusing on ensuring safety and compliance with regulations. It covers the entire aircraft development cycle, from system requirements through verification and validation. The latest revision includes new methods for safety analysis, such as Model-Based Safety Analysis (MBSA) and Cascading Effects Analysis (CEA). It is mandatory for all aircraft and systems worldwide, including emerging eVTOLs and UAVs, to demonstrate compliance with aviation regulations. This guideline aligns with ARP4761A, which was released on the same date, for safety assessment processes and offers increased flexibility in selecting validation and verification methods.
ARP4754B Applied in Jama Connect for Airborne Systems
ARP4754B and ARP4761A are both crucial guidelines, and the alignment between the two new versions has been enhanced to streamline development and safety assessments. In addition to the inclusion of the two new safety analysis methods, ARP4754B now places a stronger emphasis on identifying and mitigating unintended behaviors. It now includes consensus methods for demonstrating compliance within the development planning process and has also enhanced its flexibility in validation and verification.
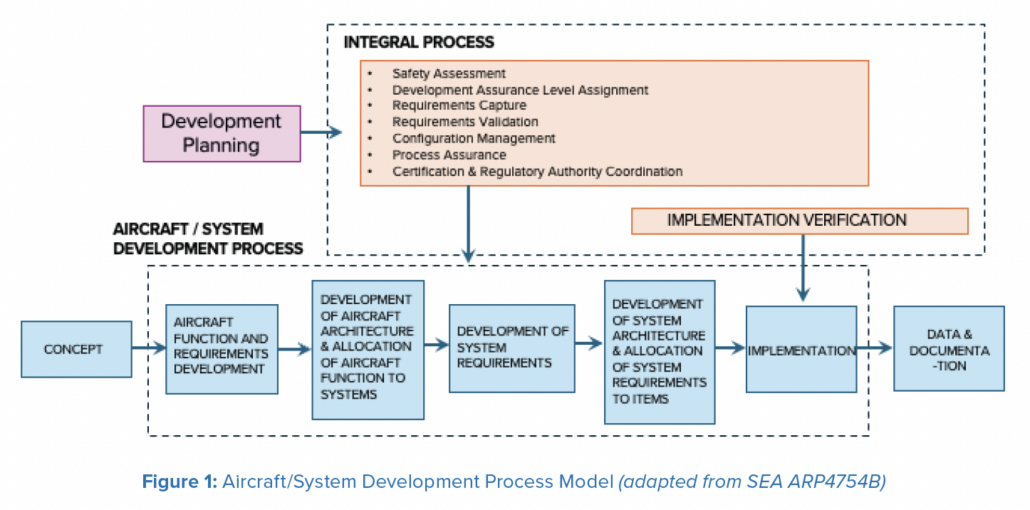
Jama Connect can be used throughout the system development process as the primary system to manage the requirements and full product traceability. Figure 1 from ARP4754B outlines the relationships between the lifecycle and integral processes, which provide guidelines for safety assessment, electronic hardware and software lifecycle processes, and the system development process described herein.
There are always numerous ways to tailor the use of Jama Connect. Here’s how the updates to ARP4754B influence requirements management and how our Airborne solution is pre-configured to support them.
1: Adoption of Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE)
- MBSE Integration: Updates encourage the use of MBSE to handle the increasing complexity of aircraft systems.
- Modeling Languages: Use of modeling languages like SysML to create detailed system models that include requirements, behavior, and structure.
Jama Connect for Airborne Systems Model-Based Techniques
- Model-Driven Requirements: Requirements are captured and managed within the Jama Connect data model, providing requirements management techniques that support model-based representations. The Solution comes pre-configured with element types that correspond to the levels of requirements called out in ARP4754B, function elements, WBS, verifications and validations, and safety-related elements. Jama Connect constrains the data to follow the traceability rules which enable rapid analysis, automated trace matrix generation, and querying and reporting.
- Synchronization of Models and Textual Requirements: Ensuring consistency between textual requirements and model-based representations requires synchronization mechanisms. Jama Connect is often used in conjunction with SysML tools and all leading vendors offer native integrations.
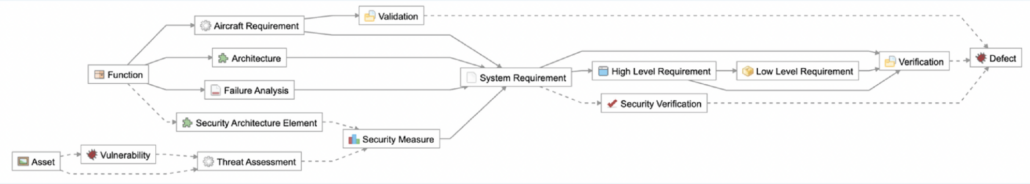
Figure 2: Model-based elements replace documents and the Jama Connect for Airborne Systems’ traceability schema maintains consistency.
RELATED: A Path to Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) with Jama Connect
2. Enhanced Integration of Safety and Requirements Management
- Safety-Driven Requirements: The updates emphasize integrating safety assessments directly into the requirements management process. This means that safety considerations become a foundational aspect of requirement definition and management.
- Iterative Feedback Loop: There is a stronger focus on creating an iterative process where safety analysis results inform requirement updates, and changes in requirements trigger reassessment of safety analyses.
Jama Connect for Airborne Systems Safety & Requirements Management Techniques:
- Traceable Within the Model: The outputs from safety analyses are captured and managed directly in Jama Connect. Our Airborne Systems solution provides the data model for a consistent trace and data strategy between safety, requirements, and tests.
- Requirements Annotation: Requirements have built-in attributes for safety-related information, such as hazard classifications and safety integrity levels.
- Tool Integration: Jama Connect integrates seamlessly with safety analysis tools such as ANSYS Medini, the LDRA tool suite and others to ensure seamless data flow and traceability between safety assessments and requirements.
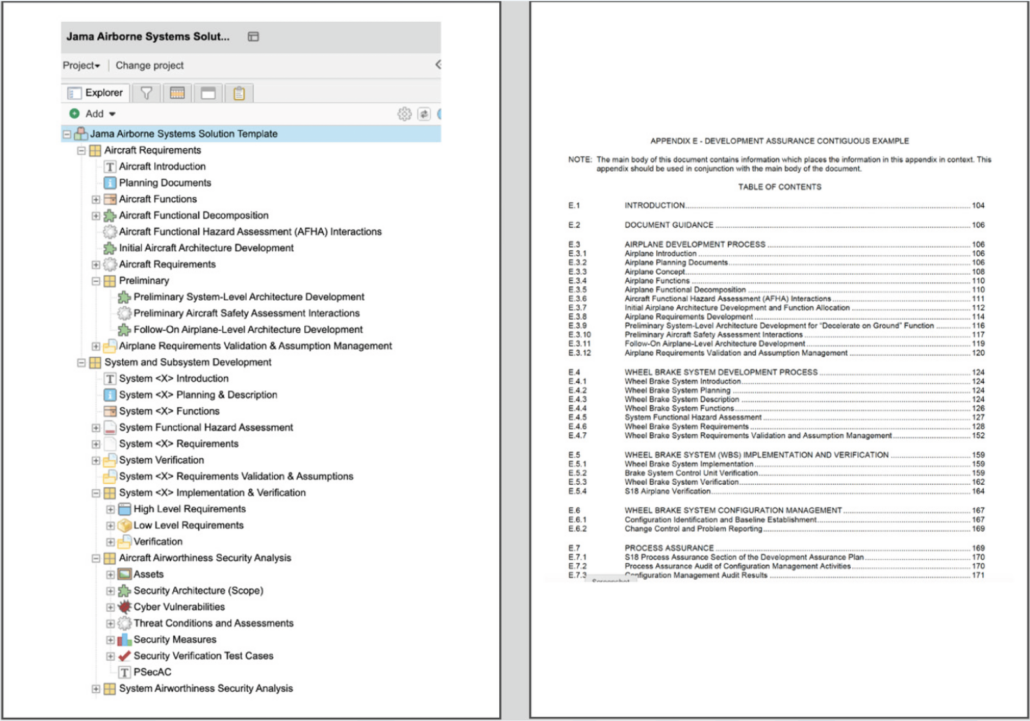
Figure 3: Jama Connect for Airborne Systems solution on the left and SAE ARP4754B (page 102) on the right.
RELATED: Cybersecurity in the Air: Addressing Modern Threats with DO-326A
3. Improved Traceability Requirements
- Bidirectional Traceability: Enhanced emphasis on maintaining bidirectional traceability between requirements, design artifacts, implementation, and verification activities.
- Traceability to Safety Objectives: Requirements must be directly linked to safety objectives and hazard analyses derived from updated safety assessment processes.
Jama Connect for Airborne Systems Solution Techniques:
- Robust Traceability Matrices: The solution comes preconfigured with views and filters required by ARP4754B. These sophisticated traceability matrices that map requirements to design elements, test cases, and safety analyses are also exportable. The Airborne Systems solution has out-of-the-box export templates that can also be tailored.
- Automated Traceability: Instead of authoring content and then creating a trace to its related content after the fact, use the “Add Related” functionality built into Jama Connect. This use of automated trace creation to manage traceability reduces the risk of human error and improves efficiency.
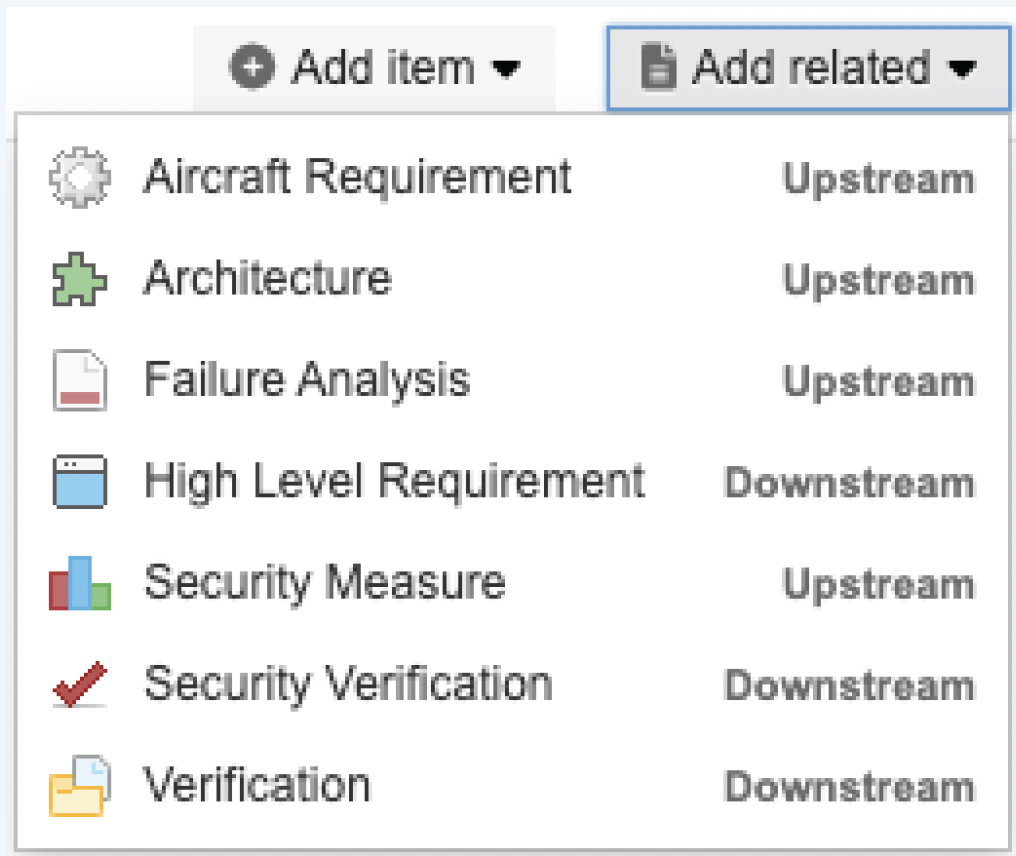
Figure 4: Constrained set of data choices ensures users create consistent traces.






![[Webinar Recap] Transform Engineering Processes: Bridge Gaps Between Teams and Tools Effectively [Webinar Recap] Transform Engineering Processes: Bridge Gaps Between Teams and Tools Effectively](https://www.jamasoftware.com/media/2025/01/Transform-Engineering-Processes.png)