EU Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) FAQs: Industry Expert Insights
Are you grappling with the intricacies of the EU Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) and searching for clear answers to your most pressing questions? Look no further!
In this blog post, we’ve teamed up with subject matter expert Saby Ágai, Senior Professional Services Consultant at Jama Software®, who will shed light on the complex world of medical device compliance.
Overview + General Information
Why was the MDD (Medical Devices Directive) updated?
Saby Ágai: MDD entered into force in 1993, 30 years ago. There have been many changes over these three decades. There have been technological changes since then, software for example has more attention now than it had 30 years ago.
Patient demographics characteristics have changed, now it is a more aging population than it was 30 years ago. Medical device safety should correspond to these changes.
MDD was primarily focused on medical device commercialization criteria rather than looking at patient safety from a holistic perspective.
What are the most important changes introduced by the EU Medical Device Regulation?
- EU MDD was focused on commercialization guardrails and market clearance criteria first.
- EU MDR accounts for the full technological landscape, establishing guardrails for the regulation, manufacturing, and commercialization of medical devices.
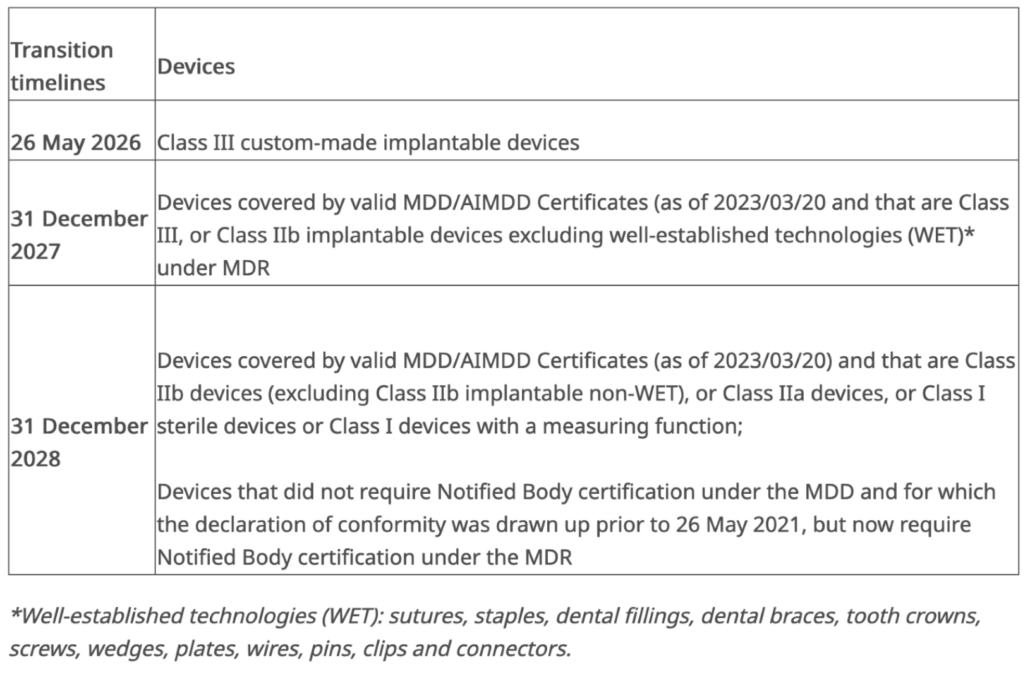
Given that timelines may continually change, what is the latest information regarding extensions?
RELATED: What the New Medical Device Regulations (EU MDR) Mean for You
Implementation/Adaptation + Need for Process Improvement
The EU MDR has changed how medical devices are covered. What opportunities and challenges might this expansion present for manufacturers?
Opportunities:
- Manufacturers can deliver to the market higher levels of safety for their medical devices.
- Manufacturers can be more aware and in control of their medical device lifecycle.
- Potentially this could result in less recalls and less rework, and fewer customer complaints. There is also an opportunity for an easier pathway to other markets like US, Canada, Japan, and others.
Challenges:
- Steep learning curve to adopt to the new regulation
- Lack of professional, lack of experiences how to adopt to the new regulations
- Optimizing efforts and resources spent on the adoption of MDR
What strategic steps should medical device companies and regulatory experts take to ensure a successful transition in light of the changes brought on by the MDR and its effect on CE markings?
Manufacturers should have a plan for MDR transition
- Expert panel of the EU could be involved to receive professional support
- Regulatory professionals should be competent to the new regulations
- Best practices across the medical industry should be utilized for the transition
How can medical device manufacturers improve their Quality Management Systems (QMS) to be better at compliance? What new approaches can be used to make business growth and product innovation possible?
New quality management processes should be developed to correspond to the requirements of the MDR. Manufacturers should also revisit their core processes including quality assurance, risk management, and post-market process to see if re-implementation needed to ensure compliance with new MDR.
Related: Learn about the continual rollout of the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In-Vitro Device Regulation (IVDR) and the impact they’re having on the medical device industry:
Data & Documentation
What impact does the EU MDR’s demand for increased device traceability and technical documentation have on promoting patient safety and regulatory visibility? What potential advantages and obstacles might exist when attempting to reach these outcomes?
Patients will benefit from the increased focus on safety and regulatory visibility on medical devices that MDR demands. On the other hand, novel technologies in medical devices may suffer from delays to be available early for patients. It is a balance though between efficiency and safety that always was there. The increased volume of technical documentation can lead to higher levels of design awareness for the manufacturers, on the other hand the increased resources needed to get there need to be financed.
How can medical device manufacturers collaborate with notified bodies and competent authorities to ensure a streamlined and efficient certification process?
There is a conflict of interest that does not allow the Notified Body and Authorities to provide consulting on MDR compliance for the same manufacturer that registered for certification. Manufacturers can help the certification process by signing up for certification on time. Manufacturers also can streamline certification processes by involving competent and experienced professionals to fulfill the Person Responsible for Regulatory Compliance (aka PRRC) role.
RELATED: CE Marking for Medical Device Software: A Step-By-Step Guide
Innovation
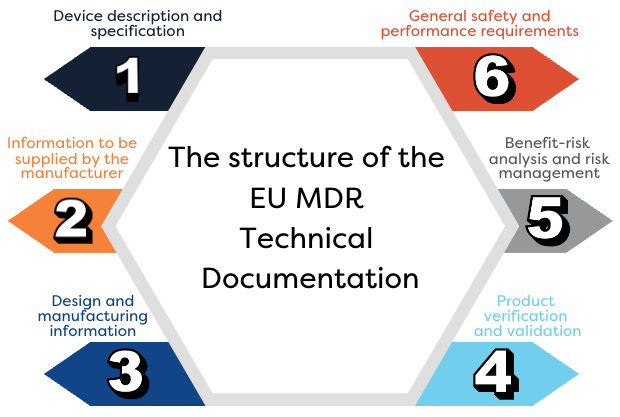
Can you explain the new EU MDR’s structure and how it supports innovation and patient safety?
Here is a great resource for that: https://www.leanentries.com/wp-content/uploads/mdr-table-of-contents.pdf. MDR is taking a holistic view on patient safety by broadening its scope to the full lifecycle of medical devices.
What are some key differential requirements that organizations will need to comply with?
- Unique Device Identification (UDI) System – European Union
- EUDAMED (European Database on medical devices) registration and documentation
- European Union
- More attention on post-market surveillance processes.
- Technical documentation:
Let’s investigate the products listed in Annex XVI of the MDR and discuss the effects this will have on both manufacturers and healthcare providers. How can stakeholders take advantage of this inclusion to create positive results?
Those products are subject to the MDR, even though those are without an intended medical purpose. These products previously were unregulated products and the MDR introduces new manufacturing and surveillance requirements. A positive result is the higher level of transparency of the design, manufacturing and post market activities of these products. Users of such products benefit from a higher level of safety when using these products.
Will the stricter regulatory requirements of the EU MDR hinder or promote innovation in the medical device industry?
There is always a balancing between introducing novel technologies to patient treatments that potentially can save or extend our life as a patient versus using only high level of safety assured medical devices. If the current MDR hinders or promotes innovation only time will tell.
How can manufacturers balance the need for compliance with the desire to bring innovative products to market in a timely manner?
Market regulations are prescriptive to the given market. Manufacturers probably will deliver slightly different functionalities for essentially the same medical devices depending on how the market regulation allows for more open for novel technologies.
Patient Safety
How does the EU MDR change clinical evaluation requirements? And how can the industry adapt to these changes while continuing to prioritize patient well-being and efficacy?
The MDR has more rigorous clinical evaluation requirements, necessitating robust clinical data to support the safety and performance claims of the device. For each device, the manufacturer must plan, establish, document, implement, maintain and update a post-market surveillance (PMS) system that is proportionate to the risk class and appropriate for the type of device. The PMS system actively and systematically gathers, records and analyses data on the quality, performance and safety of a device throughout its entire lifetime. Post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) is a continuous process that updates the clinical evaluation. It is conducted in accordance with a PMCF plan that is an element of the overall PMS plan.
What opportunities does the EU MDR present for enhancing patient safety through better data collection and analysis?
Clinical evaluation and post-market related information will be more transparent for the medical devices; therefore, manufacturers will have more opportunities to analyze device safety based on adverse events of similar types of devices.
RELATED: Buyer’s Guide: Selecting a Requirements Management and Traceability Solution for Medical Device & Life Sciences
Post-Market Surveillance
How does the increased emphasis on clinical data and post-market surveillance impact medical device manufacturers’ approach to product development and monitoring?
Clinical and post-market data collection should drive the design effort by transferring efficacy and safety related subjects back to development. Also, the analyses of similar products post market reporting enable manufacturers to enhance the safety of their medical device designs.
How can manufacturers leverage the new post-market surveillance requirements to proactively identify and address potential issues with their products?
MDR mandates and sets requirements for the post-market surveillance process. PMS process should be part of the manufacturer’s Quality Management System.
Manufacturers can use proactively the data gathered as part of the post-market activities for the following:
- to update the benefit-risk determination and to improve the risk management;
- to identify the need for preventive, corrective or field safety corrective action;
- to identify options to improve the usability, performance and safety of the device;
- to detect and report trends.
Conclusion
How will the EU MDR impact medical device companies operating outside the EU but wishing to access the European market?
For new arrivals, the new MDR is a demanding legislation to comply with in the European Union. Currently the conformity assessment bodies have limited bandwidth for new devices. Therefore, new manufacturers should assess the timing nature of their market access. For medical device companies operating outside the EU, there are further requirements set in the MDR in Article 11 on Authorized representatives.
How can Jama Software help organizations more easily comply with regulations like EU MDR?
Jama Software provides a solution for medical device manufacturers to adapt easily and to response quickly to the changes that the EU MDR demands. It’s achieved by providing best practices in medical device design in the context of the MDR.