Requirement Validation and Traceability Explained
The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Chapter 6: Requirement Validation and Traceability Explained
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Requirement Validation and Traceability Explained
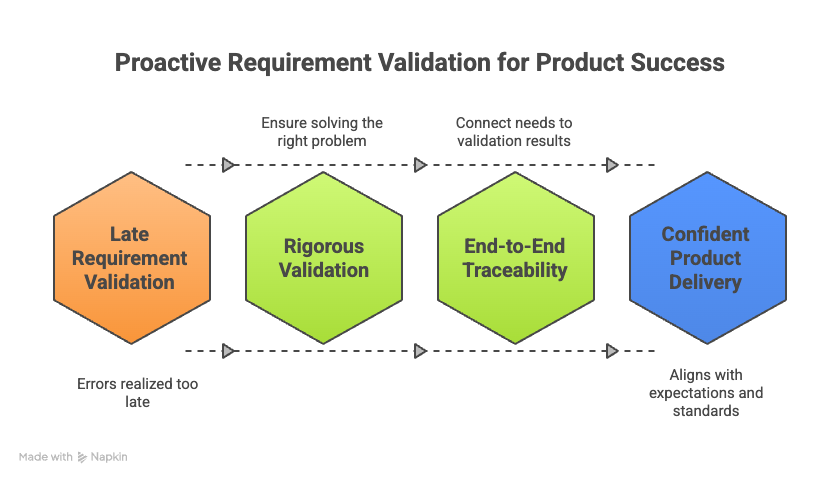
Requirement validation is frequently a stumbling block in complex product development. Teams often overlook this step or perform it far too late in the lifecycle, only realizing errors when a product fails to meet user needs or regulatory standards. While verification confirms technical accuracy, validation ensures you are solving the right problem. By combining rigorous validation with end-to-end traceability, organizations can confidently deliver systems that align with customer expectations and strict regulatory frameworks. This proactive approach transforms compliance from a chaotic burden into a competitive advantage.
What is requirement validation and traceability?
Requirement validation and traceability function as the verification mechanism for product success. While verification asks, “Did we build the product correctly based on specs?” validation asks, “Did we build the right product for the user?” Traceability connects these distinct phases, creating a clear line of sight from the initial stakeholder need to the final validation result.
Requirement validation and traceability ensure that each requirement is not only implemented correctly but also fulfills its intended business or regulatory need. Validation confirms that the product meets the user’s actual environment and usage needs, while traceability links specific requirements to test cases and results. Together, they provide clear proof that every requirement has been satisfied, reducing risk and supporting compliance. This continuous connection allows teams to detect disconnects between what was requested and what was built before they become expensive errors.
RELATED ARTICLE: Jama Connect® Features in Five: Live Trace Explorer™
Ready to Find Out More?
Our team of experts is here to answer any questions and learn how we can help enable your continued success. Get started with a free 30-day trial, or book a demo!
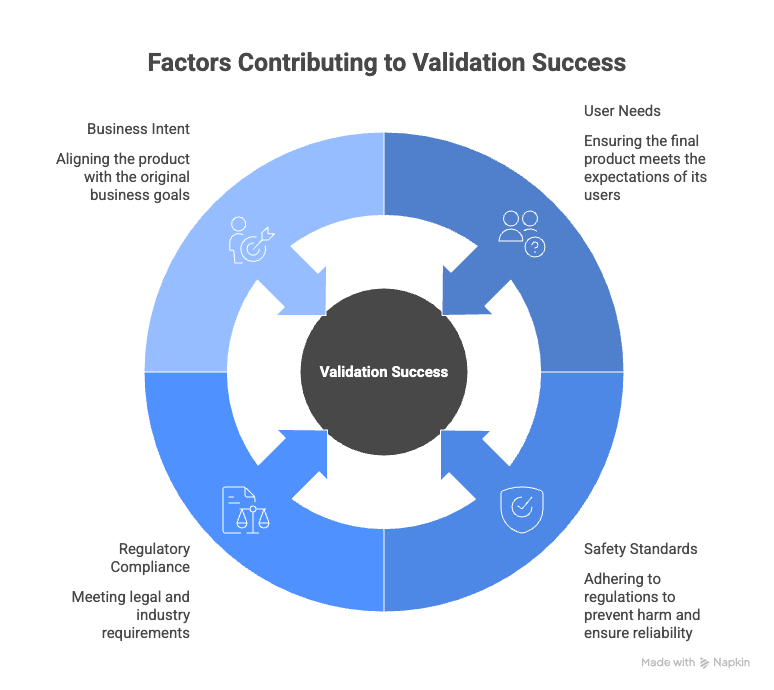
Why validation matters for compliance and quality
Validation is not just a technical checkpoint; it is a critical safeguard for quality and compliance. It ensures that the final output aligns with the original business intent rather than just the technical implementation. In highly regulated sectors, missing this step allows gaps where safety hazards or costly recalls can occur.
Validation proves critical across several key industries:
- Medical Devices: Validation demonstrates that a device meets user needs and safety standards (like FDA and ISO 13485), directly reducing patient risk.
- Aerospace and Defense: It ensures systems meet safety-critical regulations such as DO-178C, preventing catastrophic failures in complex environments.
- Automotive: Teams rely on validation to meet ISO 26262 standards for functional safety, ensuring reliable performance in autonomous and assisted driving systems.
By prioritizing validation, these industries protect their liability and ensure that every delivered requirement serves a verified purpose.
How Live Traceability™ supports validation success
Validation is most effective when requirements are continuously tracked against test results. Live Traceability™ supports validation success by automating the links between requirements, test cases, and validation results. Instead of relying on static spreadsheets or documents that quickly become outdated, Live Traceability creates a dynamic, living data model.
This approach provides real-time evidence of compliance. If a test fails or a requirement changes, the system flags the impact immediately across the entire development chain. Teams can instantly generate audit-ready reports that demonstrate every requirement has been validated. This automation reduces the risk of human oversight and ensures that no requirement is validated in isolation. Product, engineering, and QA teams share a single source of truth, enabling them to catch issues early and maintain a state of constant audit readiness.
By integrating requirement validation with Live Traceability, teams move from reactive firefighting to proactive quality management. This ensures products are safe, compliant, and market-ready. Next, we will explore the software that makes this possible in Chapter 5: Requirements Management Tools.
In This Webinar, We Discuss Jama Connect® vs IBM® DOORS® for Requirements-Driven Testing
Requirement validation and traceability ensure correct implementation and fulfillment of requirements.
Book a Demo
See Jama Connect in Action!
Our Jama Connect experts are ready to guide you through a personalized demo, answer your questions, and show you how Jama Connect can help you identify risks, improve cross-team collaboration, and drive faster time to market.