FAQs About Requirements Traceability
The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Chapter 4: FAQs About Requirements Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
FAQs About Requirements Traceability
This section serves as a quick reference guide for the most common requirements traceability questions. While the earlier chapters of this guide provide comprehensive details on implementation and strategy, these FAQs offer concise answers to core concepts. Review the definitions below for a high-level overview, and click through to the linked sections for in-depth explanations on the importance of traceability and best practices for your organization.
What is meant by requirements traceability?
Requirements traceability is the ability to track a requirement’s life throughout the entire development and testing cycle. It involves documenting the relationships between upstream requirements (like customer needs) and downstream work items (like tests and code). This ensures that every requirement is fulfilled and that every piece of code serves a documented purpose. For a deeper dive into the core definition, see [Chapter 4.1: What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained].
RELATED ARTICLE: Requirements Traceability – What are you missing?
Why is requirements traceability so important?
The importance of traceability cannot be overstated in modern systems engineering. It is the primary mechanism for proving compliance with industry standards, managing change impact, and ensuring product quality. By maintaining live traces, teams significantly reduce rework and mitigate the risk of product recalls. Traceability provides the “proof” that what was built matches what was asked for. Learn more about the business value in [Chapter 4.2: How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers].
Ready to Find Out More?
Our team of experts is here to answer any questions and learn how we can help enable your continued success. Get started with a free 30-day trial, or book a demo!
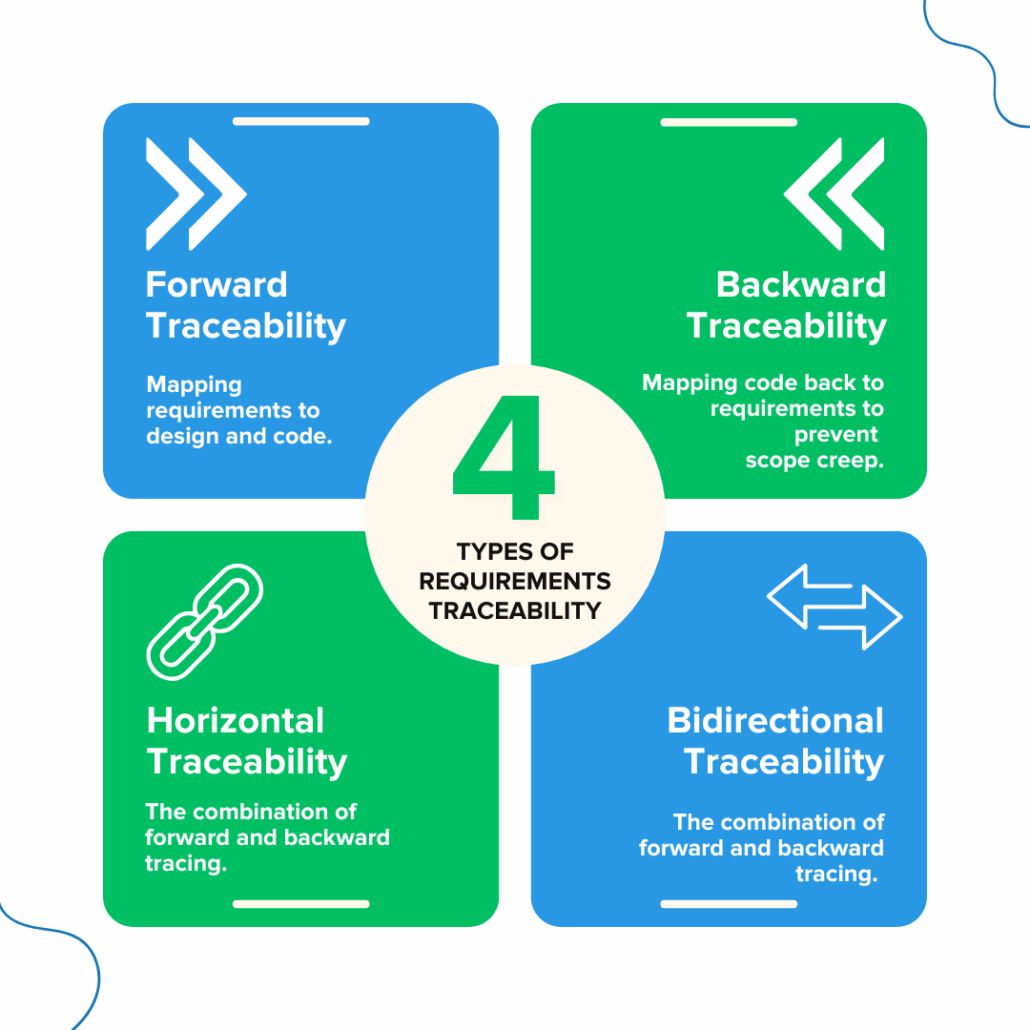
What are the four types of requirements traceability?
There are four primary types of requirements traceability that ensure complete coverage:
- Forward Traceability: Mapping requirements to design and code.
- Backward Traceability: Mapping code back to requirements to prevent scope creep.
- Bidirectional Traceability: The combination of forward and backward tracing.
- Horizontal Traceability: Linking related items at the same level (e.g., risk to requirement).
Review the mechanics of these types in [Chapter 4.5: Types of Traceability].
What is requirement validation and traceability?
Validation and traceability are inextricably linked processes used to confirm that the right product is being built. While verification checks if the product was built correctly, validation ensures the product fulfills the intended use and stakeholder needs. Traceability links validation tests directly to user requirements, providing the necessary evidence for audits and regulatory submissions. Learn more about requirements validation and traceability in this sub-chapter.
For a more robust understanding of how to automate these processes, explore the full guide or see how Jama Connect simplifies traceability management.
Traceability is the ability to track upstream and downstream relationships between requirements and other artifacts, ranging from test cases to higher-level system or subsystem requirements.
Book a Demo
See Jama Connect in Action!
Our Jama Connect experts are ready to guide you through a personalized demo, answer your questions, and show you how Jama Connect can help you identify risks, improve cross-team collaboration, and drive faster time to market.