How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Chapter 4: How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
Creating a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) is more than just a documentation exercise; it is a critical step for ensuring product quality and achieving regulatory compliance. In the previous section, we defined the purpose of an RTM. Now, we will shift focus to the practical application: how to build one that effectively tracks requirements through the development lifecycle.
Without a properly structured RTM, teams risk “orphan” requirements — features that are built but never tested — or scope creep, where features are built without a defined requirement. By following a structured approach to creating and using an RTM, you ensure that every requirement is accounted for, tested, and validated before release.
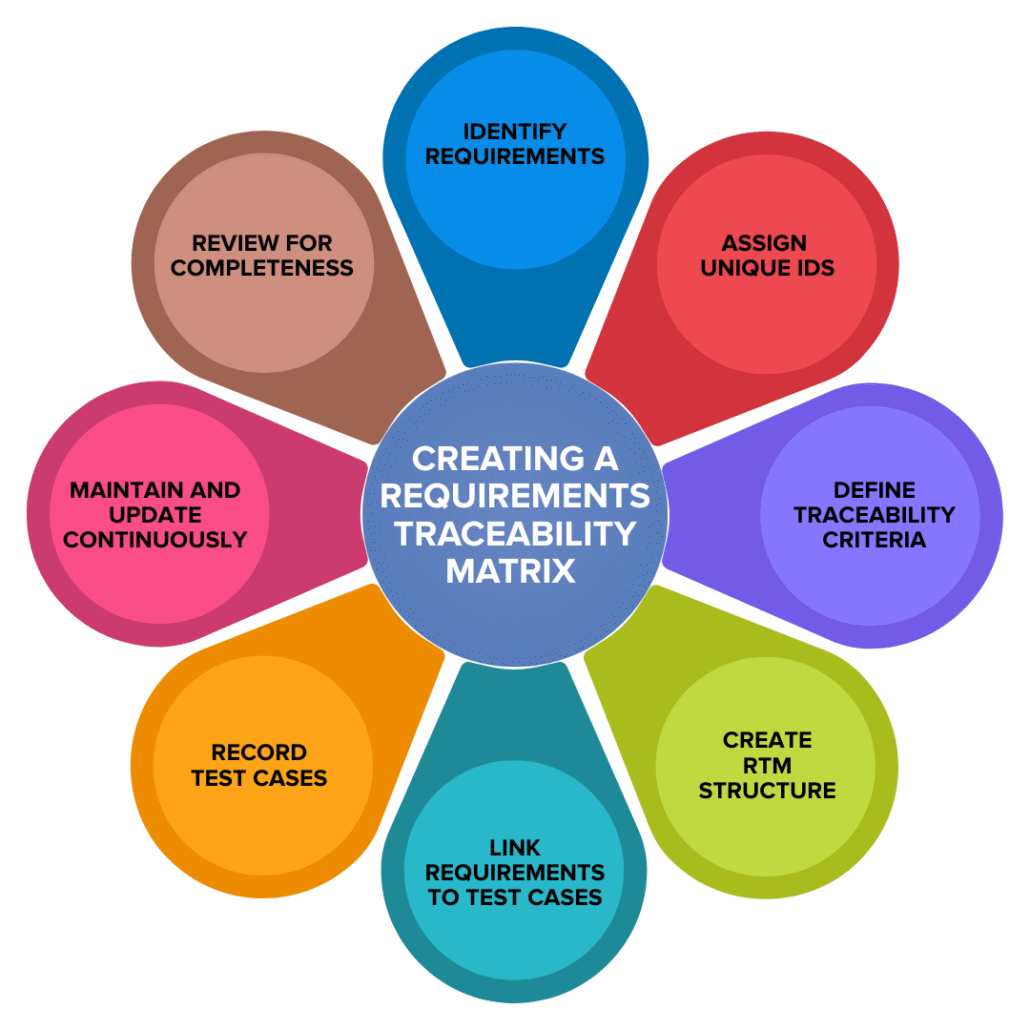
Steps to create a requirements traceability matrix
Building an RTM doesn’t need to be complex. Whether you are using a spreadsheet or a dedicated requirements management tool, teams can follow these standardized steps to ensure complete traceability:
- Identify requirements: Start by gathering all functional and non-functional requirements from stakeholders, specifications, or user stories. Ensure these are finalized and agreed upon before mapping begins.
- Assign unique IDs: Give each requirement a unique identifier (e.g., RQ-001) for easy tracking and reference. This ID allows you to trace the requirement across different documents and stages of the lifecycle.
- Define traceability criteria: Decide exactly what you need to trace. Common criteria include mapping requirements to test cases, requirements to design documents, or requirements to specific compliance standards.
- Create the RTM structure: Build your matrix. If using a spreadsheet, create columns for Requirement ID, Requirement Description, Test Case ID, and Status. Best-in-class software, like Jama Connect, will automatically generate this structure.
- Link requirements to test cases: Map each requirement to one or more test cases that validate it. This creates your “forward traceability,” ensuring that development goals are being met by testing.
- Record test results: As testing occurs, update the matrix with execution results (Passed, Failed, In Progress) for each requirement. This provides a snapshot of project health.
- Maintain and update continuously: An RTM is a living document. Keep it current throughout the project lifecycle as requirements evolve or change.
- Review for completeness: Regularly check that every requirement has at least one linked test case and that no test is “orphaned” (unlinked to a requirement).
While these steps provide the necessary structure, maintaining an RTM manually can become time-consuming as projects scale. That’s where automation becomes critical.
Ready to Find Out More?
Our team of experts is here to answer any questions and learn how we can help enable your continued success. Get started with a free 30-day trial, or book a demo!
Best practices for using a traceability matrix
Once an RTM is created, strict adherence to best practices ensures it delivers maximum value and doesn’t become a bottleneck.
- Keep it simple but complete: Avoid unnecessary complexity. Focus on essential columns like Requirement ID, Test Case ID, and Status to ensure the document remains readable and usable.
- Update continuously: Maintain the RTM throughout the lifecycle, not just at milestones. Waiting until the end of a project to update the matrix often leads to gaps in coverage and rushed documentation.
- Integrate with testing tools: Wherever possible, connect your RTM with QA systems so test results update automatically.
- Validate both directions: Ensure you have forward traceability (checking that requirements are tested) and backward traceability (checking that the code written actually serves a requirement).
- Include compliance references: For regulated industries (like medical devices or automotive), add a specific column linking requirements to standards or regulations to streamline audits.
- Use automation where possible: Manual spreadsheets are prone to human error. Using specialized software ensures accuracy, saves time, and prevents version control issues.
The real power of an RTM comes to life when applied to real-world projects, moving from theory to practice.
Example of a requirements traceability matrix in action
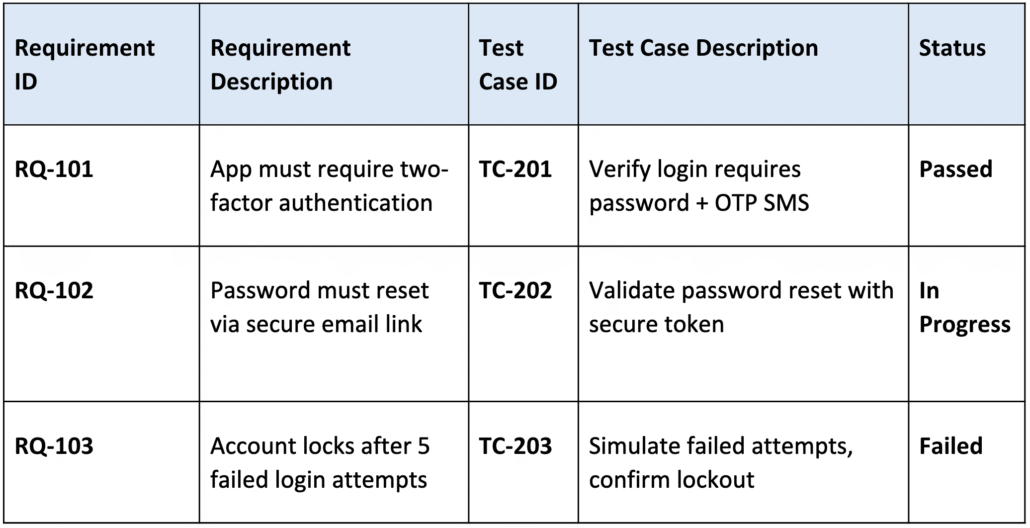
An RTM becomes most valuable when applied to tangible development scenarios. For example, consider a development team building a secure login feature for a banking app. The RTM ensures each security requirement is strictly validated through linked test cases and results.
This example shows how requirements, test cases, and results are linked in a single view, providing full visibility and compliance evidence. In this scenario, the “Failed” status on TC-203 immediately alerts the team that a critical security feature is not functioning, preventing a potential vulnerability from reaching production. Without an RTM, missing test cases or failed validations might go unnoticed until late in the project.
RELATED ARTICLE: Requirements Traceability Benchmark
Supporting Automated RTM Creation with Jama Connect
Manually creating and maintaining a requirements traceability matrix can be difficult to scale as requirements change over time. Jama Connect helps teams move beyond static spreadsheets by supporting automated traceability across requirements, test, and validation artifacts, improving visibility and alignment as development progresses.
This approach helps teams:
- Maintain traceability as requirements evolve
- Reduce manual effort associated with managing RTMs
- Improve visibility into requirement changes across teams
- Support collaboration between engineering, QA, and compliance
- Prepare for reviews and audits with greater confidence
RELATED ARTICLE: Why Live Traceability™ Matters for Medical Device Compliance
Closing
Modern teams can’t scale RTM processes manually — automation with Live Traceability™ is the new standard for success. See how Jama Connect simplifies RTM creation and compliance reporting.
In This Webinar, Learn How to Improve Traceability and Enhance Coverage with Live Trace Explorer™
Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a document in which product teams track the relationships between requirements, verification, risks and other artifacts throughout the product development process.
Book a Demo
See Jama Connect in Action!
Our Jama Connect experts are ready to guide you through a personalized demo, answer your questions, and show you how Jama Connect can help you identify risks, improve cross-team collaboration, and drive faster time to market.