How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Chapter 3: How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
Rewriting requirements for every new project can feel like reinventing the wheel, like a time-consuming and resource-draining process. Failing to reuse requirements effectively adds inefficiencies, produces inconsistencies, and increases the risk of errors.
The solution?
Adopting structured strategies for requirement reuse, allowing your team to save time, improve quality, and maintain alignment, particularly when handling multiple products or similar projects.
TL;DR: Discover methods to efficiently reuse and synchronize requirements with the right tools and processes, allowing your team to save time while maintaining traceability and compliance.
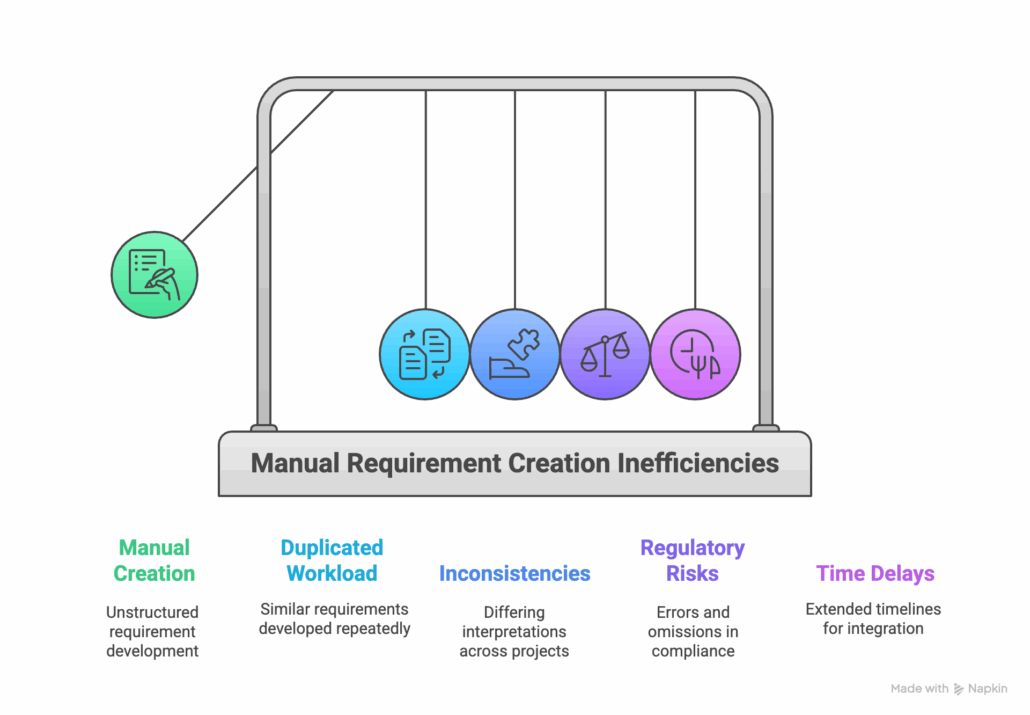
Inefficiencies in Manual Requirement Creation
The problem is all too common, and we see it with many of our customers before they switched to Jama Connect.
Without a structured reuse approach, engineers face:
- Duplicated Workload: Developing similar requirements for different projects from scratch.
- Inconsistencies: Stakeholders may interpret requirements differently across overlapping projects, jeopardizing alignment.
- Regulatory Risks: Manual duplication can lead to errors or omissions critical for compliance in regulated environments.
- Time Delays: Manually integrating existing requirements into subsequent projects significantly extends timelines.
Quick Insight: Manual replication or rewriting of requirements increases the risk of inconsistencies and costs organizations valuable time.
RELATED ARTICLE: Reuse & Sync: Jama Connect Help Guide
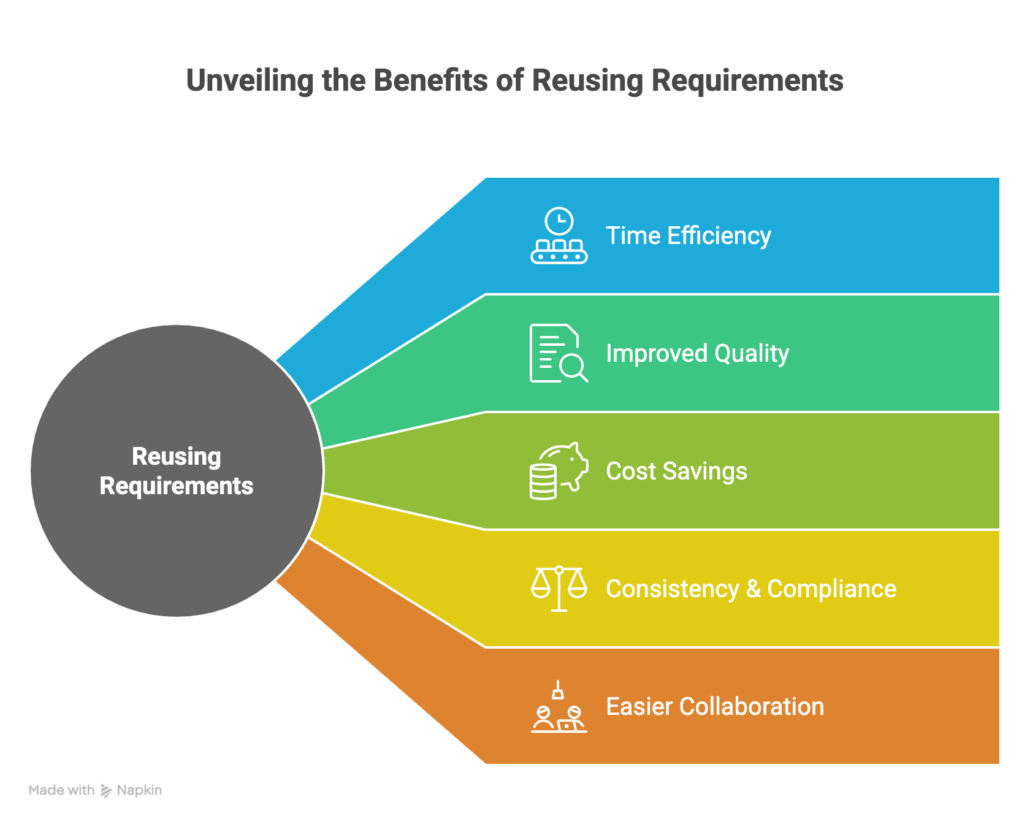
Advantages of Reusing Requirements
Reusing requirements (especially when there’s proper processes in place) ensures that previously validated and tested requirement sets get applied across relevant projects. Key benefits include:
- Time Efficiency: Pre-developed (and approved) requirements reduce administrative overhead for new projects.
- Improved Quality: Using validated, tried, and tested requirements minimizes errors.
- Cost Savings: Reduces redundant effort and resource expenditure. Not to mention the human cost of reviewing requirements that have already been validated.
- Consistency & Compliance: Promotes standardization and ensures adherence to industry regulations.
- Easier Collaboration: A centralized repository fosters alignment across teams engaging with similar requirement sets.
Bottom line: Projects and products leveraging reusable requirements benefit from streamlined processes, lower risks, and regulated alignment.
Actionable Strategies to Reuse Requirements
1. Implement Centralized Requirement Management and Repositories
A centralized repository houses validated requirements, eliminating silos, and providing easy access. Categorization and tagging aid engineers in filtering project-specific requirements seamlessly.
- Use Case: Create common libraries for frequently used compliance requirements.
- Pro Tip: Ensure the repository includes metadata like version history, tags, and applicable use cases.
2. Leverage Synchronization Tools for Real-Time Updates
Modern platforms like Jama Connect integrate requirement reuse with built-in synchronization. Synchronization ensures changes propagate instantly across reused items, maintaining traceability.
Example with Jama Connect:
- Reuse display requirements linked to verification items. Automatically sync future modifications to retain consistency.
- Use “Sync View” to track any deviations between library components and project implementations.
3. Develop Modular and Scalable Requirements
Break complex requirements into reusable templates or modules. This ensures teams can adapt modular components to new contexts without requiring full redesigns.
- Scenario: Modularize compliance standards (e.g., ISO guidelines) into scalable templates tailored for Agile or waterfall workflows.
4. Compare and Consolidate Variances Across Reused Requirements
Variations will occur in reused requirements, such as formatting differences or functional deviations. Tools like Jama Connect’s “Compare View” make it easy to align libraries while controlling variances.
- Example in Practice: During roadmap curations, compare product branch differences with traceability views to audit synchronized requirements against changes.
5. Define Governance Policies for Reusability
Design and implement approval workflows governing when, how, and who can reuse requirements.
Checklist for better governance:
- Enforce standard naming conventions
- Validate all updates before propagating changes
- Assign roles, like “Reuse Managers,” to oversee standardization initiatives
6. Reusing Test Cases
Reusing test cases is a crucial step in streamlining product development, ensuring efficiency, and maintaining consistency across projects. By leveraging existing test cases, teams can reduce redundant effort, accelerate testing cycles, and improve overall traceability between requirements and verification processes.
Checklist for effective test case reuse:
- Maintain a centralized test case repository
- Standardize test case formats for uniformity
- Map test cases to requirements for clear traceability
- Regularly review and update test cases for relevance
- Assign ownership for managing and curating reusable test cases
Is there a tool that supports scalable requirement reuse across multiple products?
Jama Connect’s Reuse and Synchronization feature allows teams to build smarter systems while speeding up delivery cycles and reducing rework risks.
Key Features:
- Copy Requirements and Their Relationships: Copy entire requirement sets along with associated verifications and tests, preserving traceability.
- Real-Time Synchronization: Maintain alignment across reused content and original source.
- Parallel Development Support: Manage variances efficiently during product branching and merging for iterative strengthening.
- Comparison Views for Diagnostics: Perform audits on reused content consistency.
- Scalability: Ideal for both startups and large enterprises scaling their development projects.
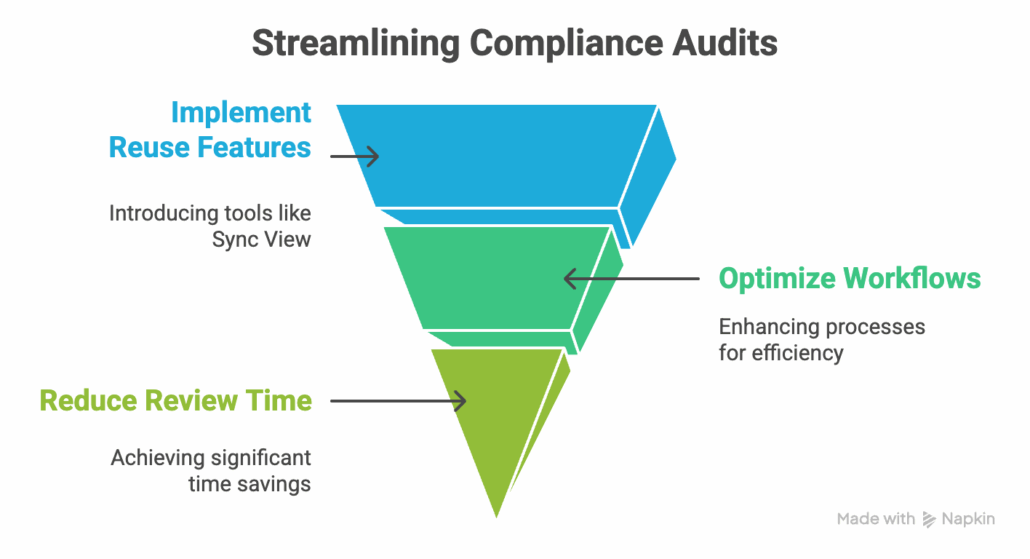
Improving Efficiency with Reuse
From managing regulatory compliance to accelerating multi-product rollouts, implementing reuse features like Sync View has decreased requirement review time by as much as 50% for Jama Connect users. Leveraging optimized workflows saves valuable hours during compliance audits, ensuring standardization across global projects.
FAQs
Q1: What types of requirements are best suited for reuse?
Functional requirements (e.g., login mechanisms), templates/autogenerated frameworks (e.g., compliance checklists), and core operational workflows offer maximum modularity and reusability.
Q2: How do I ensure reused requirements remain updated?
Enable synchronization tools like Jama Connect’s library linkage options. Establish version control workflows ensuring future edits automatically populate across downstream projects.
Q3: Will requirement reuse incur compliance risks?
No, as long as your reused elements factor in traceability tools. Trace updates retroactively for audit-ready documentation.
Effortlessly reuse and synchronize your requirements using industry-leading capabilities from Jama Connect. Start saving time, ensuring compliance, and maintaining consistency with each project iteration.
Learn More: Jama Connect Features for Reuse & Sync
Not yet a customer? Request a Demo Today
Note: This article was drafted with the aid of AI. Additional content, edits for accuracy, and industry expertise by Mario Maldari, McKenzie Jonsson, and Decoteau Wilkerson.
RELATED ARTICLE: Best Practices Guide for Writing Requirements
In this video, watch a quick demo of Reuse & Sync capabilities in Jama Connect
REUSING REQUIREMENTS with a structured approach helps your team save time, boost quality, and stay aligned—especially when managing multiple products or similar projects.
Book a Demo
See Jama Connect in Action!
Our Jama Connect experts are ready to guide you through a personalized demo, answer your questions, and show you how Jama Connect can help you identify risks, improve cross-team collaboration, and drive faster time to market.