What is Meant by Version Control?
The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Chapter 4: What is Meant by Version Control?
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Stages of Requirements Management Processes
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering in Software Engineering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 2 What is Requirements Traceability? Importance Explained
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 6 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 9 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 10 Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Definition and Purpose
- 11 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- 12 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 13 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 14 Overcoming Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability™
- 15 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 16 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 17 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 18 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 19 FAQs About Requirements Traceability
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
What is Meant by Version Control?
Version control is a critical aspect of modern product, systems, and software development, providing a structured approach to managing, tracking, and recording changes to files, projects, or items within a system over time. Whether you’re a systems engineer working on requirements for complex projects or a software developer juggling multiple code revisions, version control streamlines the process, reduces errors, and ensures teams can collaborate effectively.
In this subchapter, we’ll explore the fundamentals of version control for requirements, its importance, actionable strategies for implementation, how tools like Jama Connect empower teams, and answers to common questions.
Why is Version Control Important?
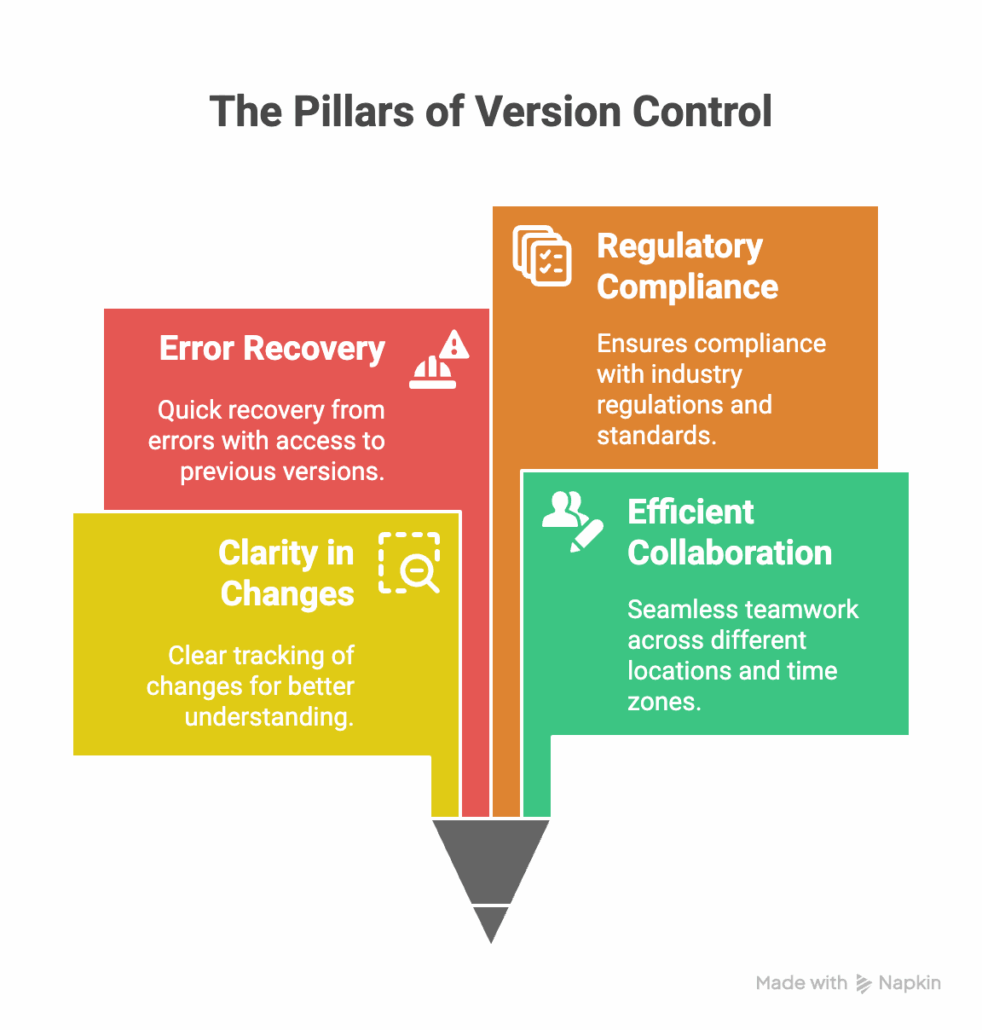
Version control plays a vital role across industries where precision, traceability, and collaboration are paramount. Here’s why it’s indispensable:
- Clarity in Changes: Version control allows teams to track what changed, who made the change, and why.
- Efficient Collaboration: Teams working across geographies can simultaneously contribute without overriding others’ work.
- Error Recovery: Access to previous file versions ensures a safety net to recover from mistakes.
- Streamlined Regulatory Compliance: Industries like medical devices or aerospace, where compliance is critical, use version control to provide documentation for audits.
Simply put, it’s a systemized approach to maintaining consistency and accountability while ensuring flexibility and adaptability.
“The version control [in Jama Connect] is second to none and the flexibility makes it easy to customize projects and exports.” – Technical Writer, Communications Company
How Does Version Control Work?
Version control systems (VCS) operate by capturing and managing changes to files or items. Below are two widely used concepts in version control:
1. Versioning
This involves creating incremental changes to individual items or files. Each saved change becomes a “version” along with associated comments and metadata.
2. Baselines
Baselines represent a snapshot of an entire project or a set of items at a particular point in time. These are commonly used to capture an approved state of a project.
Key takeaway: Baselines preserve project context, whereas incremental versions ensure detailed history tracking of single items.
“Jama Connect’s largest impact has largely been with the organization and version control management of our requirements database. Managing risks has also been very effective but using Jama Connect to manage our immense database of 10,000+ requirements has been the most helpful. ” – Systems Engineer, Aerospace & Defense
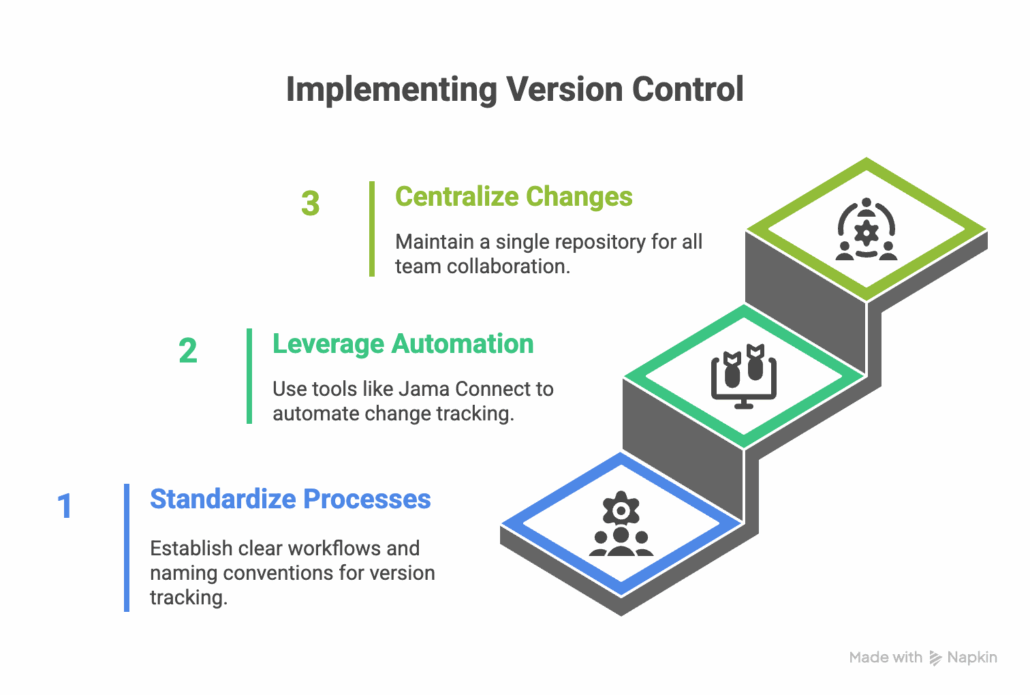
Actionable Strategies to Implement Version Control
1. Standardize Processes
- Define workflows for version tracking at both item and project levels.
- Use consistent naming conventions for files and versions.
2. Leverage Automation
- Use tools like Jama Connect to reduce manual tracking overhead and ensure every change is captured seamlessly.
3. Centralize Changes
- Maintain a single repository where all team members collaborate, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Pro Tip: Automating baselines, as offered by Jama Connect, simplifies monitoring the progression of large projects.
How Jama Connect Facilitates Version Control
Jama Connect provides robust version control capabilities tailored to address real-world challenges of systems engineers handling complex projects. Here’s how:
- Item-Level Versioning: Tracks incremental versions of items with clear comparisons highlighting changed, added, or removed data.
- Baselines for Project Snapshots: Allows teams to capture full project snapshots or subsets to preserve and compare at a point in time. Every time you initiate a review in Jama Connect, the platform automatically creates a baseline of those items.
- Seamless Collaboration: Integrates with tools to streamline updates and communication.
For a detailed walkthrough, explore Jama Connect’s features on tracking changes.
Key Insight: Automating version control with Jama Connect dramatically reduces manual effort and errors when managing revisions across multiple teams.
“The introduction of Jama within our R&D enabled an explicit traceability across the development. The versioning on single item level enables an accurate control of change. We estimate our R&D teams (several thousand engineers across the globe) spend 10-15% of their time in Jama in developing and aligning on requirements, design & architecture and test-cases formulations.” – Engineer at Infineon
RELATED ARTICLE: Jama Connect Features in Five: Baselines
Ready to Find Out More?
Our team of experts is here to answer any questions and learn how we can help enable your continued success. Get started with a free 30-day trial, or book a demo!
FAQs on Version Control
1. What’s the difference between Versioning and Baselines?
Versioning tracks changes at an individual item level, while baselines capture snapshots of entire projects or item groups for historical or review purposes.
2. How does version control improve compliance?
Version control systems create an auditable trail of changes, allowing teams to quickly generate documentation supporting regulatory audits.
3. Can version control handle scope creep in projects?
Yes. By tracking incremental changes and baselines, it becomes easier to manage adjustments, revert unwanted changes, and maintain control over evolving project scopes.
Conclusion
Whether managing software or complex systems, version control ensures teams work efficiently and collaboratively while maintaining high standards of accuracy and compliance. Tools like Jama Connect go further by automating tedious processes, providing insights, and ensuring traceability at every stage of development.
Ready to streamline your version control processes? Learn more about Jama Connect for version control.
Note: This article was drafted with the aid of AI. Additional content, edits for accuracy, and industry expertise by Mario Maldari and Kenzie Jonsson.
In This Webinar, Learn How To Eliminate Gaps and Risks with Proven Traceability Best Practices
Version Control is a system that tracks and manages changes to files, enabling collaboration, history tracking, and the ability to revert to previous versions.
Book a Demo
See Jama Connect in Action!
Our Jama Connect experts are ready to guide you through a personalized demo, answer your questions, and show you how Jama Connect can help you identify risks, improve cross-team collaboration, and drive faster time to market.