Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Fundamentals of Requirements Management
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 What is Traceability?
- 2 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 6 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 9 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 10 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 11 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 12 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 13 How to Overcome Organizational Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability
- 14 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 15 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 16 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 17 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Chapter 1: Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Fundamentals of Requirements Management
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 What is Traceability?
- 2 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 6 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 9 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 10 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 11 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 12 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 13 How to Overcome Organizational Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability
- 14 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 15 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 16 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 17 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
The quality of your requirements dictates the success of your project. Poor requirements are a primary source of project failure, leading to significant cost overruns, missed deadlines, and products that don’t meet stakeholder expectations. For systems engineers managing large-scale projects with evolving needs and diverse technologies, the challenge of maintaining high-quality requirements is constant.
This guide will help you understand the common causes of poor requirements, their costly impact on the development lifecycle, and actionable strategies to prevent them. You will learn how to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive quality assurance, ensuring your projects are built on a solid foundation.
TL;DR: This article explores how ambiguity, communication gaps, and inconsistent processes lead to bad requirements, which in turn cause costly rework and project delays. We’ll cover best practices and AI-powered tools that help systems engineers write clear, accurate, and testable requirements from the start.
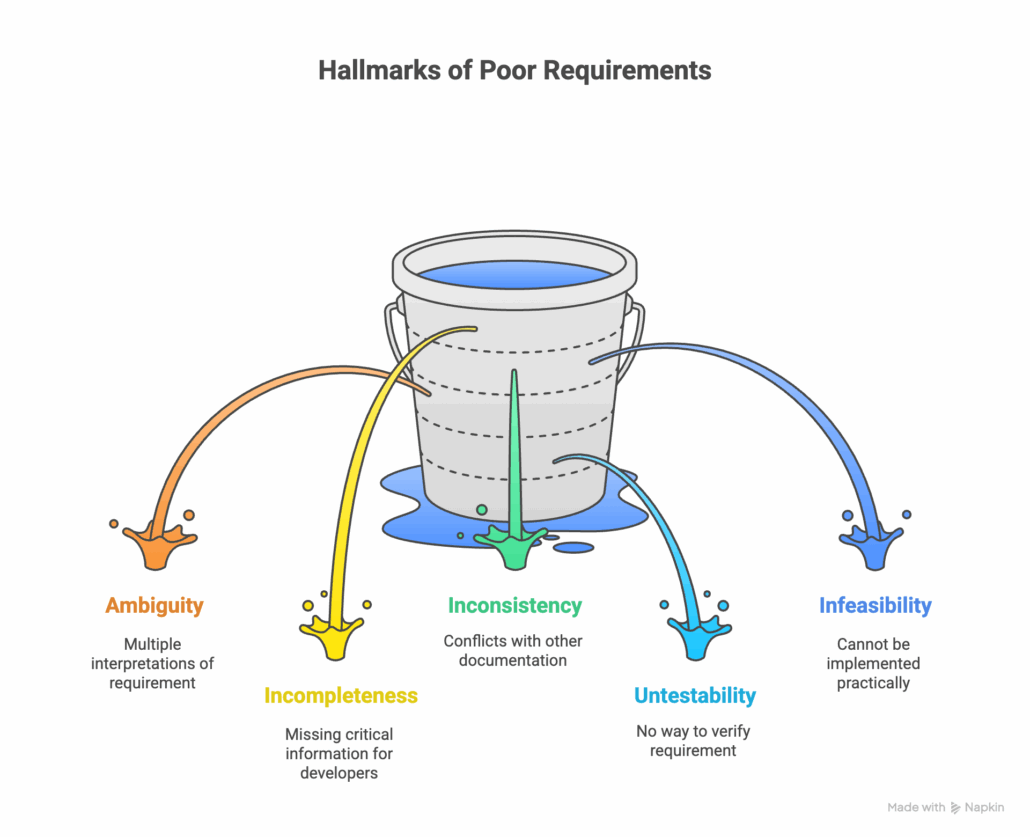
What Makes a Requirement “Poor”?
A poor requirement is any specification that is unclear, incomplete, or untestable. While a “good” requirement is clear, concise, and verifiable, a bad requirement often introduces risk and confusion. As a systems engineer, identifying these issues early is critical.
Having trouble deciphering between a good and bad requirement? Look out for some of these key characteristics of poor requirements.
The Top 5 Causes of Poor Requirements
Understanding the root causes of bad requirements is the first step toward preventing them. Most issues can be traced back to a handful of common process and communication breakdowns.
1. Ambiguity and Lack of Clarity
Vague language is the most frequent culprit. When requirements are not written with precision, teams are forced to guess the intended meaning, which almost always leads to errors. This includes undefined acronyms, subjective terminology, and poorly constructed sentences.
2. Incomplete or Missing Information
This happens when stakeholders fail to provide all necessary details. Unstated assumptions are particularly dangerous, as different team members may fill in the gaps with conflicting ideas. A requirement might specify what the system should do but omit crucial details about how it should perform under specific conditions.
3. Poor Stakeholder Communication
Complex projects involve numerous stakeholders, each with their own perspective and priorities. Without a structured process for gathering and reconciling input, the resulting requirements can be a collection of conflicting demands. This lack of a unified vision creates confusion and rework down the line.
4. Unmanaged Scope Creep
Projects naturally evolve, but when changes to requirements are not properly documented, tracked, and approved, chaos ensues. This uncontrolled expansion of project scope, known as scope creep, leads to outdated or contradictory requirements that no longer reflect the project’s goals.
5. Lack of a Standardized Process
Without a consistent format, review cycle, and authoring guidelines, requirements quality will vary wildly across teams and projects. This lack of standardization makes it difficult to manage, trace, and reuse requirements effectively, compounding inefficiencies.
The Ripple Effect: How Bad Requirements Derail Projects
The consequences of poor requirements extend far beyond the initial design phase. They create a domino effect that impacts the entire development lifecycle – and your company’s bottom line.
- Costly Rework: Defects caused by poor requirements can consume up to 85% of project rework costs. Fixing an error in the requirements phase is exponentially cheaper than fixing it after the product has been built and tested.
- Project Delays: Ambiguous or incomplete requirements force development teams to stop and seek clarification, leading to significant delays. Rework cycles further push back timelines, jeopardizing market delivery.
- Product Failure and Safety Risks: In safety-critical industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, a poorly defined requirement can lead to catastrophic system failure, posing serious risks to end-users.
- Decreased Team Morale: Nothing is more frustrating for an engineering team than spending weeks building a feature, only to find out it was based on a misunderstanding of the requirements. This cycle of rework can damage morale and reduce productivity.
A Modern Solution: Improving Requirements Quality with AI
For systems engineers, manually reviewing every requirement for clarity, consistency, and completeness is a monumental task, especially in large-scale projects. This is where modern tools can make a significant difference.
The key takeaway is that leveraging technology can transform requirements management from a manual, error-prone process into an efficient, data-driven one.
Jama Connect Advisor™ brings the power of Artificial Intelligence and Natural Language Processing directly into the requirements authoring process. It acts as an intelligent assistant for systems engineers, helping to identify and fix poor requirements in real time. By analyzing requirements against proven industry standards like the INCOSE Rules and EARS Notation, it provides immediate, actionable feedback.
With Jama Connect Advisor, you can:
- Eliminate ambiguity by flagging vague terms and suggesting precise alternatives.
- Ensure completeness by identifying missing information.
- Standardize authoring across all teams with consistent, rule-based guidance.
- Monitor quality over time with detailed scores and reports to drive continuous improvement.
RELATED ARTICLE: Jama Connect® Features in Five: Jama Connect Advisor™
Ready to Find Out More?
Our team of experts is here to answer any questions and learn how we can help enable your continued success. Get started with a free 30-day trial, or book a demo!
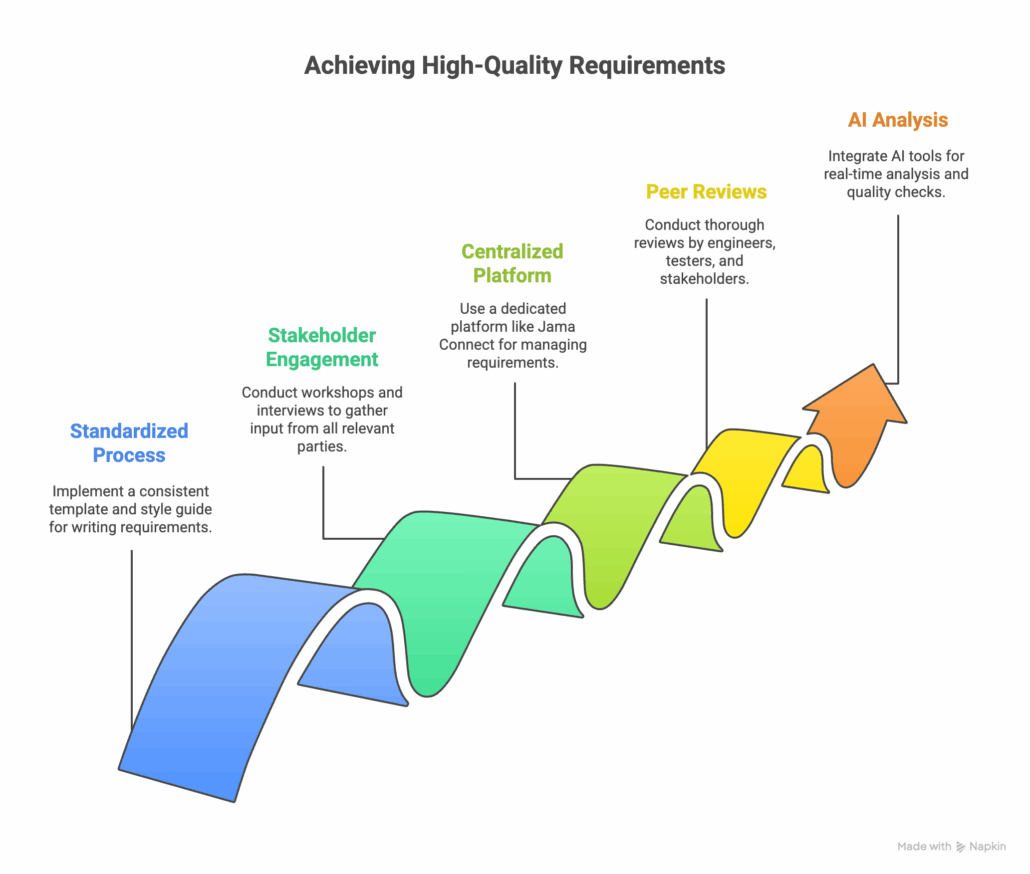
Best Practices for Preventing Poor Requirements
Here are five actionable steps you can take to improve requirements quality in your organization.
- Step 1: Establish a Clear, Standardized Authoring Process. Create and enforce a consistent template and style guide for writing requirements. This ensures everyone follows the same structure and terminology.
- Step 2: Engage All Stakeholders Early and Often. Use structured workshops and interviews to gather input from all relevant parties. Ensure a formal sign-off process is in place to confirm a shared understanding.
- Step 3: Use a Centralized Requirements Management Platform. Move away from documents and spreadsheets. A dedicated platform like Jama Connect provides a single source of truth, making it easier to manage, trace, and collaborate on requirements.
- Step 4: Implement Peer Reviews and Formal Inspections. Before a requirement is approved, it should be reviewed by other engineers, testers, and stakeholders to catch any ambiguities or inconsistencies.
- Step 5: Leverage AI-Powered Tools for Real-Time Analysis. Integrate tools like Jama Connect Advisor to automatically analyze requirements as they are written, providing instant feedback and quality checks.
FAQs
Q1: What is the most common cause of poor requirements?
The most common causes are ambiguity and poor communication. Vague language that can be interpreted in multiple ways, combined with a lack of clear and consistent dialogue between stakeholders and engineering teams, is a primary driver of bad requirements.
Q2: How can I measure requirements quality?
Requirements quality can be measured against several criteria, including clarity, completeness, consistency, testability, and feasibility. Modern tools like Jama Connect Advisor automate this process by providing a “quality score” for each requirement based on analysis against established rulesets.
Q3: What are INCOSE rules for writing requirements?
The International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) provides a set of guidelines and best practices for writing effective requirements. These rules help ensure that requirements are clear, correct, unambiguous, and verifiable. You can learn more about them in the Jama Connect Advisor help documentation.
Take Control of Your Requirements
Don’t let poor requirements derail your next project. By understanding their causes and implementing a proactive strategy for quality, you can save time, reduce costs, and deliver successful, complex systems. See how Jama Connect Advisor can help you write clear, accurate, and high-quality requirements from the start.
In This Video, Watch a Demonstration of Jama Connect Advisor™
Poor Requirements are a primary source of project failure, leading to significant cost overruns, missed deadlines, and products that don’t meet stakeholder expectations.
Book a Demo
See Jama Connect in Action!
Our Jama Connect experts are ready to guide you through a personalized demo, answer your questions, and show you how Jama Connect can help you identify risks, improve cross-team collaboration, and drive faster time to market.