How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Fundamentals of Requirements Management
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 What is Traceability?
- 2 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 6 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 9 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 10 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 11 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 12 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 13 How to Overcome Organizational Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability
- 14 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 15 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 16 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 17 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
Chapter 8: How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Fundamentals of Requirements Management
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 8 Guide to Poor Requirements: Identify Causes, Repercussions, and How to Fix Them
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 9 How to Reuse Requirements Across Multiple Products
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 What is Traceability?
- 2 How is Traceability Achieved? A Practical Guide for Engineers
- 3 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 4 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 5 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 6 What is Meant by Version Control?
- 7 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 8 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 9 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 10 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 11 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 12 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 13 How to Overcome Organizational Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability
- 14 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 15 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 16 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 17 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Can You Track Requirements in Jira?
- 7 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- Overview
- 1 What is Systems Engineering?
- 2 How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
- 3 The Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
- 4 What is MBSE? Model-Based Systems Engineering Explained
- 5 Digital Engineering Between Government and Contractors
- 6 Digital Engineering Tools: The Key to Driving Innovation and Efficiency in Complex Systems
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- 14. Semiconductor Development
- 15. AI in Product Development
- Glossary
How Do Engineers Collaborate? A Guide to Streamlined Teamwork and Innovation
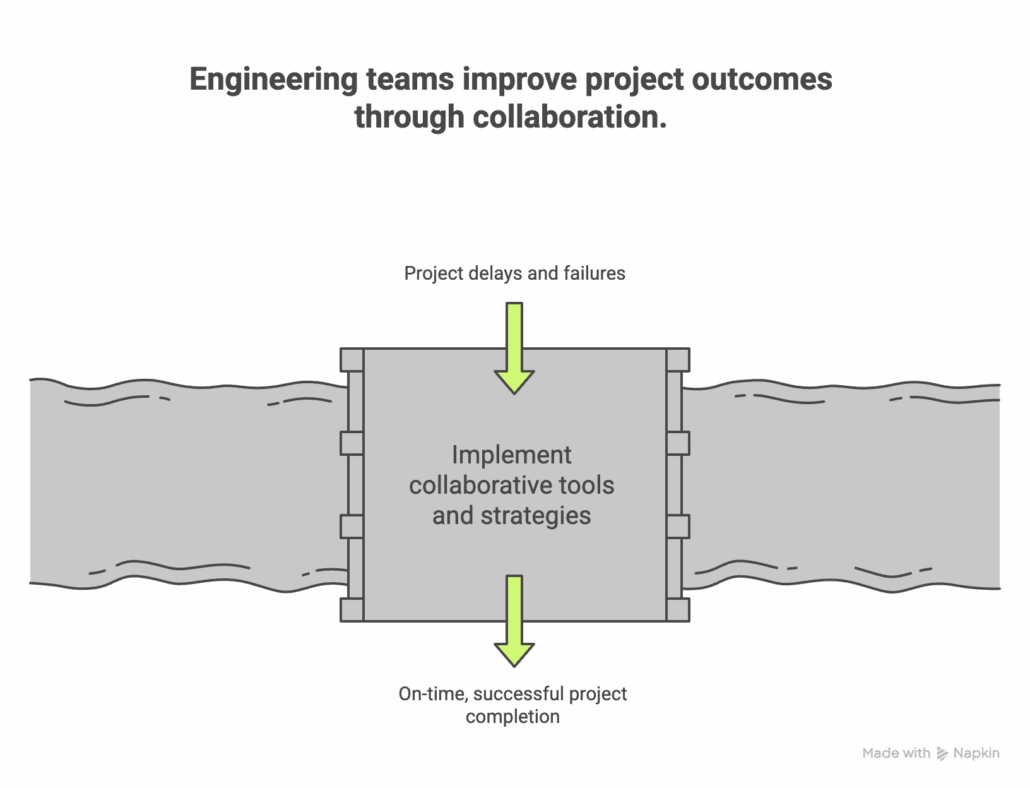
Efficient collaboration is the cornerstone of successful engineering projects. As systems become increasingly complex, engineers must navigate communication barriers, integrate diverse tools, and maintain alignment within cross-functional teams. Research indicates that poor collaboration and miscommunication account for up to 30% of project delays and failures in engineering fields. Additionally, a study by McKinsey reveals that organizations with highly collaborative teams are 20% more likely to meet performance goals and adhere to project timelines. Source
Without effective collaboration, critical issues like missed requirements and delayed timelines can arise, highlighting the importance of structured communication and teamwork in engineering success.
TL;DR: Collaborative tools and strategies dramatically enhance engineering outcomes by fostering alignment, improving efficiency, and minimizing errors.
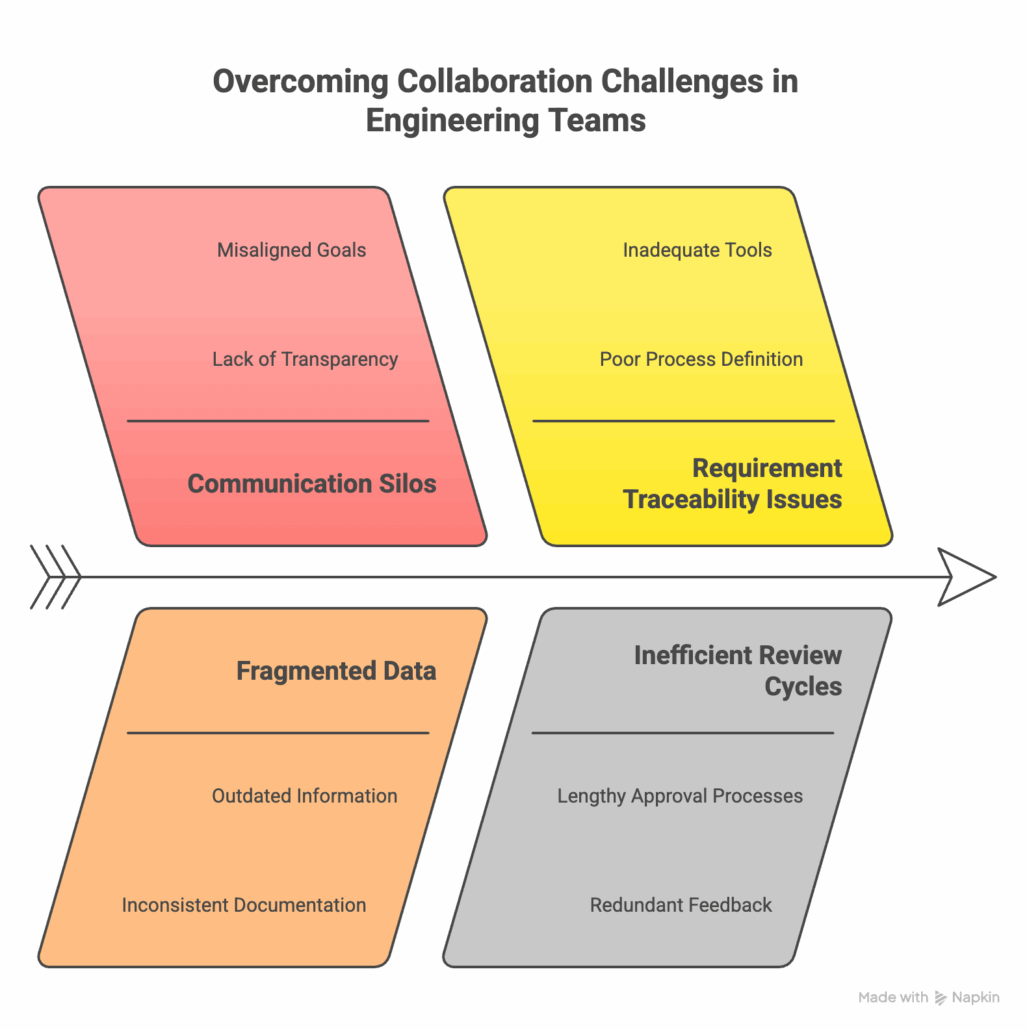
Engineer Collaboration: The Challenges
Before understanding solutions, let’s address the common collaboration hurdles engineering teams face:
Engineering teams often work in environments requiring high levels of precision, creativity, and coordination. However, these teams are frequently composed of individuals with diverse specializations, spanning software, hardware, design, and more. This cross-disciplinary nature, while invaluable, introduces complexities when aligning goals, priorities, and processes. Additionally, many engineering projects are fast-paced and rely on iterative development cycles, leaving little room for miscommunication or errors. Without strong collaboration, teams can find themselves working in silos, leading to mismatched expectations, delayed deliverables, or even product failures. The increasing reliance on remote work and distributed teams has further amplified these challenges, adding physical and temporal separation to the equation. Therefore, addressing collaboration challenges head-on is not just beneficial — it is essential to ensure engineering teams can deliver high-quality results efficiently.
1: Communication Silos
Poor communication within teams can lead to misunderstandings and inefficiencies that hinder overall performance. Communication silos occur when individuals or groups within an organization fail to openly share information, updates, or feedback with other stakeholders. This lack of transparency can result in duplicated efforts, overlooked details, and a misalignment of goals. For engineering teams, these silos could mean that crucial design considerations or development updates are not relayed effectively, leading to issues later in the workflow. To overcome communication silos, it is crucial to foster a culture of openness and encourage regular updates between all team members. Implementing collaborative tools like shared workspaces, messaging platforms, and regular stand-up meetings can help bridge gaps and create a more cohesive flow of information. By breaking down these barriers, teams can ensure better alignment and improved outcomes.
2: Fragmented Data
This fragmentation often leads to confusion, as team members may struggle to determine which version of a document is the most up-to-date or accurate. It can also result in wasted time as employees search through numerous platforms or rely on incomplete or outdated information to make decisions. To address this issue, organizations should aim to consolidate documentation into a centralized repository, ensuring that all relevant data is easily accessible and consistently maintained. Leveraging tools that integrate with existing workflows can further streamline this process, reducing the time spent navigating between platforms and minimizing the risk of errors. Establishing clear guidelines for document management and assigning ownership for updates can also help maintain consistency and reliability across teams.
3: Requirement Traceability Issues
Effective requirement traceability begins with establishing a well-defined process that links requirements to their corresponding design, implementation, and testing phases. This ensures that all requirements are accounted for at every stage of the project lifecycle. Utilizing specialized tools, such as requirement management software, can greatly enhance traceability by automating the tracking process and providing real-time updates. Additionally, creating a detailed traceability matrix allows teams to visualize the relationships between requirements and project deliverables, making it easier to identify gaps or misalignments. Regular audits and reviews of the traceability framework can further solidify compliance and maintain high-quality outputs, ensuring that no requirement is overlooked or improperly addressed.
4: Inefficient Review Cycles
Lengthy, manual approval processes hinder project agility and can lead to significant delays in meeting deadlines. When review cycles are not streamlined, teams may encounter bottlenecks, miscommunication, or redundant feedback, which slows progress and reduces overall productivity. To address this, organizations should consider implementing automated workflows or approval tools that enable faster decision-making and transparent collaboration. Establishing clear review timelines and assigning designated reviewers can also enhance efficiency by ensuring that tasks are addressed promptly and consistently. By optimizing review cycles, teams can maintain momentum, minimize delays, and deliver high-quality results within the desired timeframe.
Key Insight: Addressing collaboration challenges enables teams to focus on innovation instead of fighting organizational inefficiencies.
RELATED ARTICLE: Requirements Traceability – How to Go Live
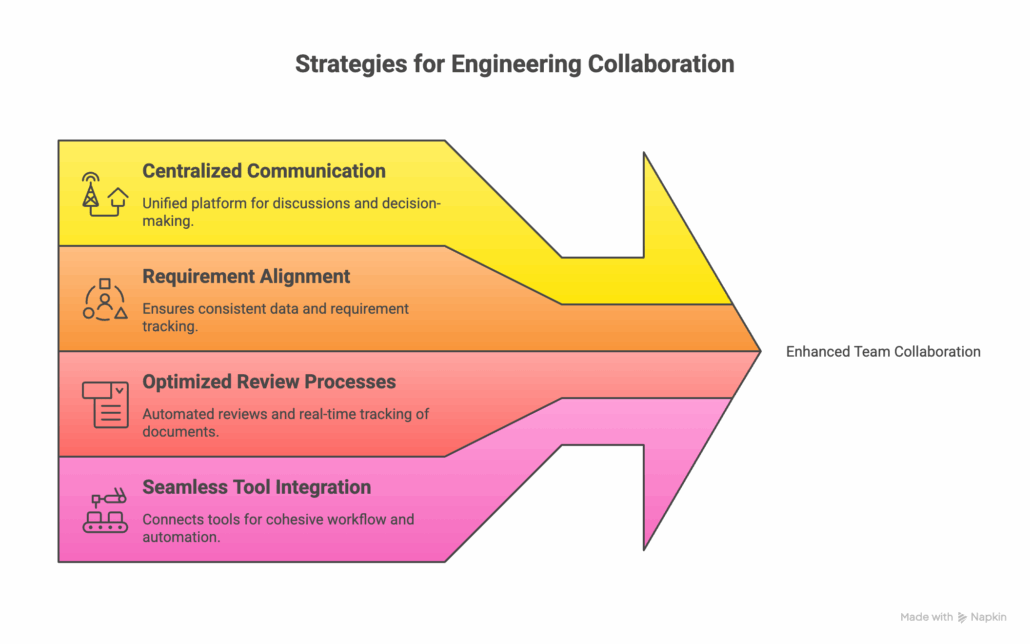
Actionable Collaboration Strategies for Engineers
1. Centralize Communication
Use tools like Jama Connect to create a central hub where discussions, updates, and decision-making are readily accessible.
Implement real-time communication platforms that integrate email threads, task comments, and meeting notes into one system.
Pro Tip: Streamlined communication reduces errors caused by outdated or missing information.
2. Align Requirements with Team Goals
Maintain a single source of truth — a centralized space that ensures all team members work with the same updated data.
Jama Connect’s robust traceability features track requirement changes and resolve gaps early in the development cycle.
3. Optimize Review Processes
Shift from manual approval workflows to automated reminders and role-specific dashboards.
Utilize software that tracks document reviews in real time and highlights critical blockers.
4. Integrate Tools Seamlessly
Opt for tools that connect with existing systems like Jira, Slack, and GitHub to enable a cohesive workflow without switching platforms.
Automate cross-system updates to eliminate manual transfers between platforms.
Bottom Line: Integration and automation prevent bottlenecks and improve the speed at which teams deliver high-quality products.
“In my opinion Jama Connect is a high-quality tool due to its robust features, user-friendly interface, and the way it streamlines requirement management. It offers exceptional traceability, collaboration (review), and reporting capabilities.” – Sekhar Ghandikota, Senior Engineer at Ford Motors
Ready to Find Out More?
Our team of experts is here to answer any questions and learn how we can help enable your continued success. Get started with a free 30-day trial, or book a demo!
How Jama Connect Enhances Engineering Collaboration
Centralized Platform for Seamless Communication
Jama Connect serves as a single source of truth, empowering teams to align on requirements, track open issues, and capture decisions in real time. Remote and cross-functional teams stay updated effortlessly without the risk of fragmented communication.
Real-Time Visibility and Traceability
The Live Trace Explorer™ is like a map for your engineering workflow. It highlights gaps, tracks progress and ensures that teams adhere to all regulations and requirements during the development process.
Customizable Workflows
Adapt Jama Connect to fit your team’s specific needs. Whether you’re managing complex supply chains or aligning multi-disciplinary teams, having flexible workflows ensures efficiency and proper alignment.
“Jama Connect is a strong requirements management software with very powerful traceability and team collaboration. It is also easy to organize projects and edit items.” – Ander Solorzano, Principal Systems Engineer at Astrobotic
Integration-Friendly
Jama Connect integrates with tools engineers already use, such as Jira or Atlassian suites. This enables smooth transfer of information, speeding up decisions while avoiding repetitive manual tasks.
Case in Point: Teams hard-pressed for compliance documentation found that centralized traceability reduced audit prep time by 50%. (Source)
Customizable Workflows
With Jama Connect’s visual workflow editor, teams can create custom workflows to match their unique processes. This not only streamlines communication but also ensures consistency across projects. Teams can easily modify workflows as needed, enabling adaptability in ever-changing projects.
“Over the last 14 years, Jama Connect has served as our primary tool for requirement management, test management, and as a collaboration platform for our development projects.” – Lien Bäcker, Systems Engineering – Application Consultant at Gira
RELATED ARTICLE: Ensure Product Quality with These Review Process Best Practices
FAQs About Engineering Collaboration
1. What are the best tools for improving engineering collaboration?
Tools like Jama Connect are purpose-built for engineering collaboration, enabling traceability, communication alignment, and integration with tools like Jira and GitHub.
2. How can engineers reduce miscommunication in global teams?
Using a centralized documentation system ensures all project members can access the latest data, minimizing discrepancies caused by time zone or language gaps.
3. Why is integrating tools crucial for engineering teams?
Integration reduces silos by creating a connected ecosystem, saving time and ensuring all updates are captured within a unified workflow.
4. How can I track engineering requirements more effectively?
Leverage tools offering traceability features, like Jama Connect, to map requirements across the lifecycle, ensuring no critical step is overlooked.
5. What’s the role of real-time collaboration in product engineering?
Real-time tools foster quicker decision-making and issue resolution, reducing project delays and promoting innovation.
Ready to elevate your engineering collaboration game? Explore Jama Connect and discover how innovative tools can empower your team to deliver faster, smarter, and better.
Jama Connect Collaboration Tutorial
How to Overcome Complex Development Challenges
Note: This article was drafted with the aid of AI. Additional content, edits for accuracy, and industry expertise by Kenzie Jonsson and Mario Maldari.
In This Webinar, Learn More About Key Systems Engineering Skills
Engineering collaboration is the structured teamwork and communication that fosters alignment, improves efficiency, and minimizes errors, enabling successful project outcomes in increasingly complex systems.