Best Practices for Verification and Validation in Product Development
In the competitive landscape of modern product development, ensuring the reliability and quality of the product is essential to meet customer – and stakeholder – expectations and regulatory requirements. Verification and validation (V&V) are two crucial processes that play a pivotal role in achieving these goals. V&V are systematic methods that assess a product’s adherence to specifications and its ability to perform as intended. In this article, we will delve into the best practices for verification and validation in product development, exploring the key steps, methodologies, and benefits of each process.
Understanding Verification & Validation
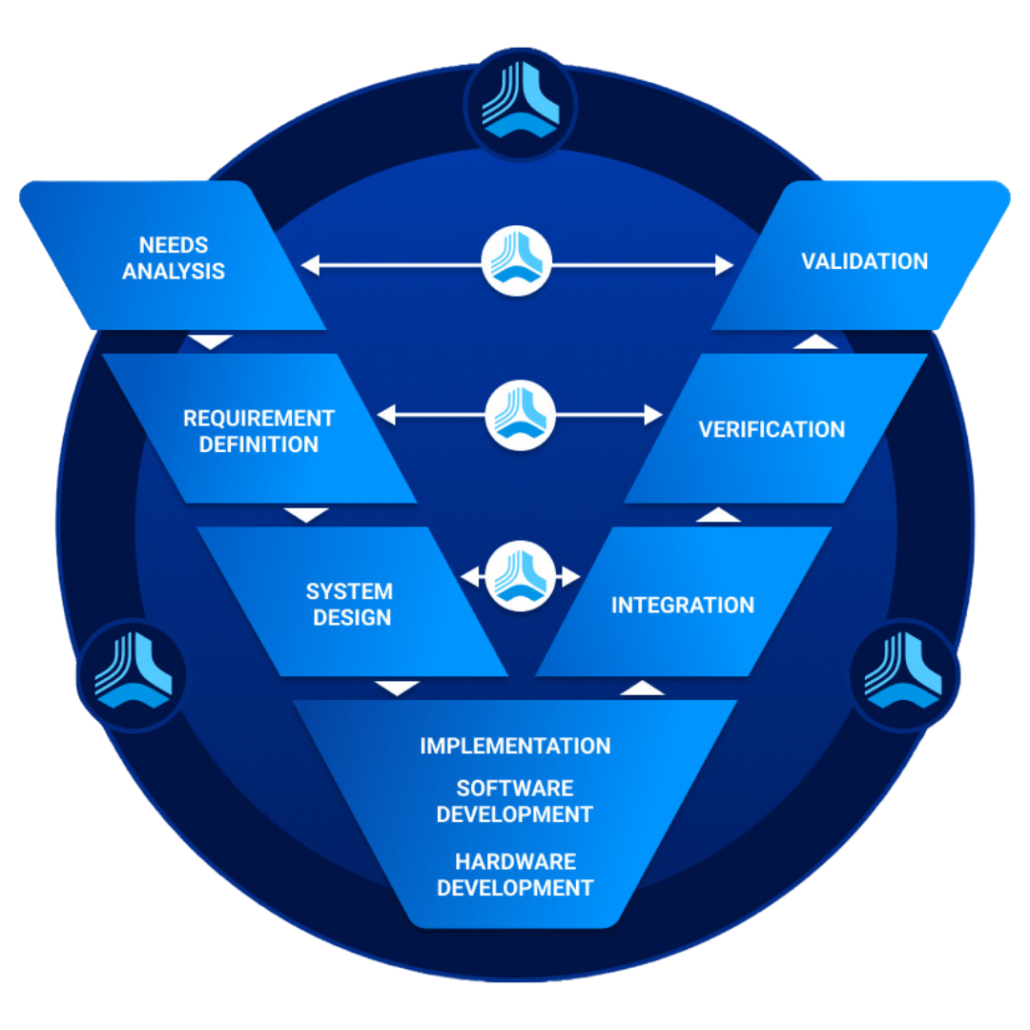
Before delving into the best practices, it is essential to clarify the distinction between verification and validation. Verification focuses on assessing whether a product meets its design specifications, ensuring that each component and feature works as intended. On the other hand, validation is concerned with evaluating whether the product fulfills its intended use and customer needs. In essence, verification confirms if the product is designed correctly, while validation confirms if it is the right product for the intended application.
RELATED: Five Key Design Control Practices that Improve Compliance and Help Develop Better Products
Incorporating V&V Early in the Development Lifecycle
To maximize the effectiveness of verification and validation, these processes must be integrated into the product development lifecycle from its early stages. By starting V&V activities early, potential issues can be identified and resolved before they escalate, reducing costs and time-to-market. Early involvement also allows for feedback to be incorporated into the design, leading to a more robust and reliable final product.
Clearly Defined Requirements
Well-defined requirements are the foundation of successful verification and validation. During the requirements gathering phase, it is vital to engage stakeholders and subject matter experts to create clear, measurable, and unambiguous specifications. These requirements serve as the baseline against which the product will be verified and validated. Proper documentation and version control are critical to ensure that changes to requirements are tracked effectively. Additionally, the later in the development process that requirements get changed, many times because they weren’t written well the first time, the more costly it is due to downstream impacts such as rework in verification and validation.
RELATED: Plutora: Verification vs Validation: Do You know the Difference?
Utilizing Various V&V Techniques
Product development teams should employ a mix of V&V techniques to comprehensively assess the product’s quality. Some commonly used methods include:
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing, including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing, to verify that each component and the product as a whole performs as expected.
- Simulation: Use computer simulations to evaluate the product’s behavior in various scenarios, particularly for complex systems or when physical testing is impractical or cost prohibitive.
- Prototyping: Building prototypes early in the development process allows for real-world testing, uncovering potential design flaws and usability issues.
- Peer Reviews: Encourage regular peer reviews of design documents, code, and other artifacts to catch errors and improve the overall quality of the product.
- Model-based Design: Utilize model-based design approaches, such as Model-Driven Architecture (MDA), to create detailed models that can be verified before implementation.
Risk-Based Approach
Incorporate a risk-based approach into V&V activities to focus resources on critical areas. Identify potential risks associated with product failure and prioritize verification and validation efforts accordingly. This approach ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, concentrating on areas with the most significant impact on product performance and safety.
Independent Verification and Validation (IV&V)
Consider engaging external experts or teams for independent verification and validation. External parties can provide an unbiased assessment of the product, uncovering issues that internal teams might overlook due to familiarity or assumptions. Independent verification and validation bring additional expertise and ensure a higher level of confidence in the product’s quality.
RELATED: How to Achieve Higher Levels of the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI)
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Implementing CI/CD practices allows for continuous verification and validation throughout the development process. Automated testing and deployment pipelines can quickly detect regressions and integration issues, ensuring that the product remains stable and reliable throughout its evolution.
Documenting V&V Activities
Comprehensive documentation of all verification and validation activities is essential for compliance, knowledge retention, and continuous improvement. Properly documented V&V processes help maintain a historical record of changes, failures, and resolutions, facilitating future product iterations and troubleshooting.
V & V are integral to successful product development, ensuring that products meet the required specifications and perform as intended. By adopting best practices such as early integration, clear requirements, a mix of v&v techniques, risk-based approaches, and continuous verification, companies can create high-quality, reliable products that customers love and gain a competitive edge in the market. Moreover, investing in verification and validation from the outset of development can save time and resources, prevent costly delays, and lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty in the long run.
- Bosch and the Chiplet Revolution: Enabling Software-Defined Mobility - February 24, 2026
- Requirements Management Software Jama Connect Breaks Records for Scalability - February 9, 2026
- Next Generation Nuclear: Reactor Innovations Shaping 2025 - November 11, 2025